Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur (Physics) Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 - Sources Of Energy Part 2
Part 2
Page No 142:
Question 36:
The minimum speed of wind necessary for the satisfactory working of a wind generator to produce electricity is about:
(a) 15 km/h (b) 25 km/h (c) 35 km/h (d) 45 km/h
Answer:
(a) 15 km/h
The minimum speed of wind should be 15km/h for the satisfactory working of a wind generator.
Page No 142:
Question 37:
If the solar constant is 1.4 kW/m2 then solar energy recived by 1m2 area in one hour is:
(a) 5040 J (b) 504.0 kJ (c) 5040 kJ (d) 5.04 kJ
Answer:
© 5040 kJ
Solar constant = 1.4 kW/m2 1 hour = 60 × 60 sec = 3600 sec Therefore, energy = 1.4 kJ/s/m2 × 3600 s = 5040 kJ
Page No 142:
Question 38:
A solar cooker may not cook food if
(a) the solar cooker is not placed in the shade (b) the glass sheet cover of solar cooker is not closed (c) a convex mirror reflector is not used (d) the food containers of insulting material are not used
Answer:
(b) the glass-sheet cover of the solar cooker is not closed
The glass sheet prevents the sunlight incident on it from being reflected back.
Page No 142:
Question 39:
A large coal-fired power station produces 2000 MW of electrical energy. A wind turbine with 33 m blades can produce 300 kW.
(a) How many turbines would be needed to replace the power station? (b) Why, in actual practice, this number of turbines could not replace the coal-fired power station?
Answer:
(a) Electrical energy from the power station = 2000 MW = 2000000 kW Energy produced by the wind turbine = 300 kW Therefore, number of turbines needed = 2000000/300 = 6666.\67 Hence, 6667 turbines will be needed.
(b) In the thermal power plant mentioned, coal is burnt to produce electricity. Therefore, the quantum of electrical energy produced is fixed. A windmill produces electrical energy depending on the speed of wind, which may vary from time to time. Therefore, wind turbines cannot replace the coal-fired thermal power plant.
Page No 142:
Question 40:
In a solar water heater, why is the storage tank placed at a higher level than the solar panel containing coils?
Answer:
In a solar water heater, the storage tank is placed at a higher level than the solar panel containing coils because hot water is lighter and rises up.
Page No 142:
Question 41:
In many applications, solar cells are connected to rechargeable batteries. Why is this so?
Answer:
Solar cells are connected to rechargeable batteries to store the electricity that we obtain with the help of these cells. The stored electricity can be used later; for example, it can be used at night, when there is no sunlight.
Page No 142:
Question 42:
(a) Solar cells are used to provide the electric current to charge the batteries of a car driven by an electric motor. Describe the energy changes which take place. (b) What differences would you expect in the charging of car batteries (i) in bright sunlight (ii) on a cloudy day (iii) at night?
Answer:
(a) The solar cells convert the energy from sunlight into electrical energy. This electrical energy is converted into chemical energy when the car batteries are charged. When these charged batteries are used, the chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. In the last stage, this electrical energy is converted into kinetic energy for the car by the electric motor that drives the car.
(b) (i) In bright sunlight, the car batteries are charged quickly. (ii) On a cloudy day, the car batteries are charged very slowly. (iii) At night, the car batteries cannot be charged as there is no sunlight.
Page No 148:
Question 1:
What substance is obtained as a residue when wood is burned in a limited supply of air?
Answer:
When wood is burnt in a limited supply of air, a black substance called charcoal is obtained as a residue.
Page No 148:
Question 2:
Name one source of energy which is not derived from solar energy directly of indirectly.
Answer:
Geothermal energy is not derived from solar energy directly or indirectly. It is the heat energy obtained from the hot rocks present inside the earth.
Page No 148:
Question 3:
What name is given to the heat energy obtained from hot rocks inside the earth?
Answer:
Geothermal energy is the heat energy obtained from the fission of radioactive materials present in the hot rocks inside the earth.
Page No 148:
Question 4:
Name the agent which decomposes animal dung into biogas.
Answer:
A micro-organism called 'anaerobic bacteria' decomposes animal dung into biogas. Oxygen is not required for this decomposition.
Page No 148:
Question 5:
Which component of biogas is used as a fuel?
Answer:
Methane is the major constituent of biogas that is used as a fuel.
Page No 148:
Question 6:
Name the constituents of biogas.
Answer:
The constituents of biogas are the following. 1. Methane 2. Carbon dioxide 3. Hydrogen 4. Hydrogen sulphide
Page No 148:
Question 7:
Which of the following is needed for the formation of biogas from cow-dung and which not? Water, Oxygen
Answer:
Water is needed and oxygen is not. Biogas is formed by the anaerobic degradation of cow dung in the presence of water but in the absence of oxygen.
Page No 148:
Question 8:
Name the clean fuel which can be obtained from cow-dung.
Answer:
On the decomposition of the organic matter in cow dung, a clean fuel, 'biogas', is obtained.
Page No 148:
Question 9:
Apart from cattle dung, what other substances can be added to a biogas plant?
Answer:
Apart from cattle dung, plant wastes can be used as a raw material in a biogas plant.
Page No 148:
Question 10:
Name any three forms of energy which could be harnessed from the sea.
Answer:
The following are the three forms of energy that can be harnessed from the sea. 1. Tidal energy 2. Wave energy 3. Ocean thermal energy
Page No 148:
Question 11:
Write two forms in which solar energy manifests itself in sea.
Answer:
The two forms of energy in which solar energy manifests itself in the sea are sea wave energy and ocean thermal energy.
Page No 148:
Question 12:
Write the full from of OTE.
Answer:
The full form of OTE is 'ocean thermal energy'.
Page No 148:
Question 13:
What is the function of anaerobic micro-organisms such as anaerobic bacteria in a biogas plant?
Answer:
In a biogas plant, the function of anaerobic micro-organisms such as anaerobic bacteria is the degradation of animal wastes in the presence of water.
Page No 148:
Question 14:
State whether the following statement is true or false: Tidal energy is one of the forms in which solar energy manifests itself in oceans.
Answer:
False. Tidal energy is not one of the forms of energy in which solar energy manifests itself in oceans.
Page No 148:
Question 15:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
(a) Biomass is another form in which ……….. energy manifests itself. (b) Tidal waves build up and recede ……….. a day.
Answer:
(a) Biomass is another form in which solar energy manifests itself. (b) Tidal waves build up and recede twice a day.
Page No 148:
Question 16:
(a) What is biomass? Give three examples of biomass. (b) Name the biomass which is still widely used as a source of heat energy in many household of our country.
Answer:
(a) Biomass Biomass is organic matter that is used as a fuel to produce energy. Examples: Wood, agricultural wastes and cow dung.
(b) Wood is one of the biomass resources that is still widely used as a source of heat energy in many households in our country.
Page No 148:
Question 17:
What are the two ways in which cow-dung can be used as a fuel? Which of them is better and why?
Answer:
The two ways in which cow dung can be used as a fuel are given below. 1. Cow-dung cakes can be used as a fuel for cooking food. 2. Biogas can be made from cow dung for use as a smokeless fuel.
Biogas is a better fuel as it does not cause air pollution. After extracting biogas, the cow dung can still be used as a manure because it continues to retain all the nutrients that plants need.
Page No 149:
Question 27:
(a) What is biogas? Name the major component of biogas. (b) What are the raw materials used for making biogas? (c) Describe the construction and working of a biogas plant with the help of a labelled diagram. (d) Write any two uses of biogas. (e) Write any two advantages of using biogas.
Answer:
(a) Biogas is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide. The major component of biogas is methane. Up to 75 per cent of biogas consists of methane gas.
(b) Biogas is produced by using raw materials such as animal wastes and plant wastes in the presence of water.
©
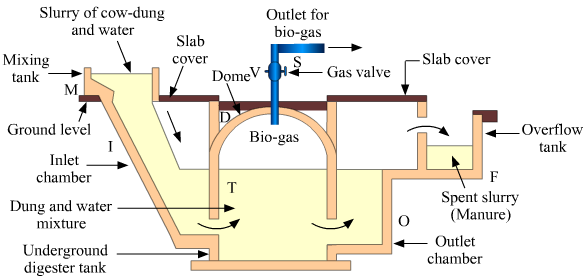
Construction of a biogas plant A biogas has an underground tank shaped like a well. It is called a digester and is made of bricks and cement. The dome of the digester acts as a storage facility for biogas. On the top of the dome, there is a gas outlet 'S' with a valve 'V'. A sloping inlet chamber 'I' is situated on the left side, and on the right side, there is a rectangular outlet chamber 'O'. The function of the inlet chamber is to introduce fresh dung slurry into the digester tank and that of the outlet chamber is to facilitate the removal of the spent slurry after the extraction of biogas. Working A slurry is made in the mixing tank by mixing cow dung and water and then fed into the digester tank through 'I'. The digester is filled up to the cylindrical level, the dome being left free for the collection of biogas. In 50-60 days, the cow dung undergoes degradation by anaerobic bacteria in the presence of water but in the absence of oxygen, with the gradual evolution of gas. The biogas that is formed gets collected in the dome and exerts pressure on the slurry in the tank for its removal through the outlet chamber.
(d) Two uses of biogas are given below.
1. As a fuel for cooking food 2. As a fuel for lighting
(e) Two advantages of using biogas are the following.
1. Biogas is a clean fuel with a high calorific value, so it is a viable alternative to fossil fuels. 2. Large-scale utilisation of biowastes and sewage for producing biogas is a safe and efficient method of waste disposal and a source of energy.
Page No 149:
Question 28:
(a) What is geothermal energy? (b) What is the source of heat contained in geothermal energy? (c) Explain how, geothermal energy is used to generate electricity. (d) State two advantages of geothermal energy. (e) State two disadvantages of geothermal energy.
Answer:
(a) Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the heat energy obtained from the fission of radioactive materials present in the hot rocks inside the earth.
(b) The hot rocks present below the surface of the earth are the sources of the heat provided by geothermal energy.
© The hot rocks inside the earth heat the underground water and turn it into steam. As more and more steam is formed between the rocks, it gets compressed to high pressures. A hole is drilled into the earth up to the hot rocks and a pipe is put into it. The steam present around the rocks comes up through the pipe at high pressure, which turns the turbine of a generator and thus produces electricity.
(d) Two advantages of geothermal energy are given below. 1. It is economical to use. 2. It does not cause any pollution.
(e) Two disadvantages of geothermal energy are given below. 1. It is available only in areas where there are hot rocks near the surface of the earth. 2. Deep drilling into the earth to obtain geothermal energy is technically very difficult and expensive.
Page No 149:
Question 29:
Which of the following is not an example of a biomass energy source?
(a) wood (b) biogas (c) atomic energy (d) cow-dung
Answer:
(c) atomic energy
Atomic energy is considered to be coming from atoms.
Page No 149:
Question 30:
Most of the sources of energy that we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the sun's energy?
(a) wind energy (b) geothermal energy (c) fossil fuels (d) biomass
Answer:
(b) geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the heat energy from the hot rocks present inside the earth and does not come directly or indirectly from the sun's energy.
Page No 149:
Question 31:
The constituent of biogas which makes it an excellent fuel is:
(a) butane (b) methane (c) propane (d) ethane
Answer:
(b) methane
Up to 75 per cent of biogas consists of methane gas, which makes it an excellent fuel.
Page No 149:
Question 32:
The major component of biogas is:
(a) hydrogen (b) butane (c) hydrogen sulphide (d) methane
Answer:
(d) methane
The major component of biogas is methane gas. Up to 75 per cent of biogas consists of methane.
Page No 149:
Question 33:
Which of the following is more environment friendly??
(a) burning of diesel (b) burning of coal (c) burning of charcoal (d) burning of wood
Answer:
(c) burning of charcoal
Charcoal does not produce smoke while burning, so it is more environment friendly than the other fuels mentioned.
Page No 149:
Question 34:
Which one of the following is not renewable energy technology?
(a) solar cells (b) windmills (c) nuclear power (d) tidal power
Answer:
(c) nuclear power
Nuclear power is a non-renewable form of energy, because nuclear materials are limited and hence we will run out of them one day.
Page No 149:
Question 35:
The rise of sea-water during high tide is caused by the gravitational pull of the:
(a) Sun (b) Earth (c) Moon (d) Mars
Answer:
(c) moon
High tide is the rise of sea water due to the gravitational pull of the moon.
Page No 149:
Question 36:
One of the following is not required in the formation of biogas in a biogas plant. This is:
(a) cow-dung (b) water (c) oxygen (d) anaerobic bacteria
Answer:
(c) oxygen
Oxygen is not required for the production of biogas.
Page No 149:
Question 37:
The fuel which is not obtained from biomass is:
(a) firewood (b) cow-dung cakes (c) coke (d) charcoal
Answer:
(c) coke
Coke cannot be obtained from biomass.
Page No 149:
Question 38:
The non-renewable source of energy among the following is:
(a) hydroelectricity (b) sewage gas (c) natural gas (d) gobar gas
Answer:
(c) natural gas
Natural gas is a non-renewable source of energy. The others are renewable sources.
Page No 149:
Question 39:
Geothermal energy is produced by the:
(a) fission of radioactive materials (b) burning of coal inside the coal mines (c) combustion of natural gas deep inside the earth (d) fusion of radioactive substances
Answer:
(a) fission of radioactive materials
Geothermal energy is obtained by the fission of radioactive materials that are naturally present in the hot rocks inside the earth.
Page No 149:
Question 18:
How is charcoal prepared? Explain why, charcoal is a better fuel than wood.
Answer:
When wood is burnt in a limited supply of air, water and other volatile materials present in it are removed, and a black substance called charcoal is left behind.
Charcoal is a better fuel than wood for the following reasons. 1. Charcoal produces more heat on burning than an equal mass of wood. 2. Charcoal does not produce smoke while burning, whereas wood produces much smoke and causes air pollution. 3. Charcoal is a compact fuel that is easy to handle.
Page No 149:
Question 19:
Compare and contrast biomass and hydroelectricity as sources of energy.
Answer:
| Biomass | Hydroelectricity | |
| 1. | Biomass energy is generated from organic matter including wood, agricultural waste and cow dung. | Hydroelectricity is produced from the potential energy of water stored at a height. |
| 2. | Biomass energy can only be used for heating and cooking. | Hydroelectricity can be used for running all types of electrical appliances. |
| 3. | No special device is required to produce energy from biomass. | Hydroelectricity can be produced by establishing a hydroelectricity plant. |
Page No 149:
Question 20:
Why is biogas considered an ideal fuel for domestic use?
Answer:
Biogas is considered an ideal fuel for domestic use for the following reasons:\
1. It does not cause air pollution as it burns without smoke.\ 2. It produces a large amount of heat per unit mass.\ 3. It is a clean fuel as it burns completely without leaving behind any residue.\ 4. It is cheaper than most common fuels.
Page No 149:
Question 21:
(a) Explain how tidal energy can used to generate electricity? (b) Why is tidal energy not likely to be a potential source of energy?
Answer:
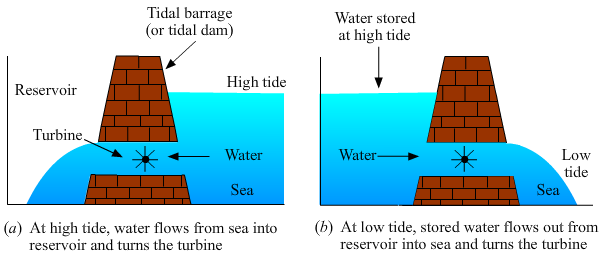
(a) The power of the rise and fall of the sea level (high tide and low tide) can be harnessed to generate electricity. During high tide, when the level of water in the sea is high, sea water flows from the sea into a reservoir at a dam and turns turbines. The turbines then turn generators to produce electricity. During low tide, when the level of sea water is low, the sea water stored in the dam reservoir is allowed to flow out into the sea. This also turns the turbines and produces electricity.\
(b) Tidal energy is not likely to be a potential source of energy for the following reasons.\
1. The rise and fall of sea water during high and low tides are not enough to generate electricity on a large scale.\ 2. Very few sites are suitable for building tidal dams.
Page No 149:
Question 22:
State two ways in which the energy of sea-waves can be harnessed.
Answer:
Two ways in which the energy of sea waves can be harnessed are the following.\
1 By setting up floating generators in the sea, which would move up and down with the sea waves. This movement would drive the generators to produce electricity.\ 2. By letting the sea waves move up and down inside large tubes. As the waves move up, the air in the tubes is compressed. This compressed air can be used to turn the turbines of a generator to produce electricity.
Page No 149:
Question 23:
What is meant by ocean thermal energy? Explain how ocean thermal energy can be used to generate electricity.
Answer:
Ocean thermal energy
The energy that is generated using the difference between the temperatures of water at the surface of the ocean and at deeper levels is called ocean thermal energy.\
To generate electricity, we use ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) power plants for which a temperature difference of 20 degrees Celsius between the surface water and the water at deeper levels is needed. In this process, the warm surface water of the ocean is used to boil a liquid such as ammonia or chlorofluorocarbon. The high-pressure vapours obtained are used to turn the turbine of a generator to produce electricity.
Page No 149:
Question 24:
What are the limitations of energy that can be harnessed from the sea?
Answer:
The limitations of the energy that can be harnessed from the sea are as follows.
1. Very strong waves are required to obtain electricity from wave energy. Such strong waves are not available in the sea all the time.\ 2. Tidal energy depends on the relative positions of the earth, the moon and the sun.\ 3. To harness ocean thermal energy efficiently, the difference between the temperatures of the surface water (hot) and the water at a depth (cold) must be 20ºC or more.\ 4. Very few sites are suitable for building tidal dams.
Page No 149:
Question 25:
Suggest a safe and efficient method for the disposal of biowastes and sewage materials. How is this method advantageous to us?
Answer:
Biowastes and sewage can be disposed of by using them in large gas plants to produce biogas and manure.\ This method is advantageous to us for the following reasons.\ 1. It is a safe method for large-scale utilisation of biowaste.\ 2. The biogas produced can be used as a fuel.\ 3. Good quality manure can be obtained by this method.
Page No 149:
Question 26:
Which of the following sources of energy are not derived from the sun? Biomass, Wind, Ocean thermal energy, Geothermal energy, Nuclear fuels, Hydroelectricity, Wave energy, Coal, Petroleum, Tidal energy
Answer:
The forms of energy that are not derived from the sun are geothermal energy, nuclear energy, hydroelectricity and energy obtained from coal and petroleum.\
Geothermal energy is the heat energy obtained from the fission of radioactive materials present in the hot rocks inside the earth. Nuclear energy comes from the nucleus of an atom. Hydroelectricity is obtained from the flow of water.
Page No 150:
Question 40:
The harnessing of which of the following leads to the destruction of large eco-systems?
(a) thermal power\ (b) tidal power\ (c) hydro power\ (d) geothermal power
Answer:
(c) hydropower\
Hydropower projects have many adverse affects on the surroundings and the environment.
Page No 150:
Question 41:
Which of the following is not a consequence of establishing hydroelectric power plants?
(a) displacement of people\ (b) production of methane\ (c) occurrence of floods\ (d) ecological disturbance
Answer:
© occurrence of floods\
All the other given problems can be the consequences of establishing hydroelectric power plants.
Page No 150:
Question 42:
A certain form of energy is available due to the difference in the temperature of water at the surface of the ocean and its deeper levels.\
(a) Name the form of energy.\ (b) Is this energy ultimately derived from the sun or not? (c) Explain how this form of energy can be converted into electricity.\ (d) What is the minimum temperature difference in water at the surface of ocean and its deeper level which is required to operate power plants based on this energy?
Answer:
(a) Ocean thermal energy\ (b) Yes. The water at the surface of an ocean gets heated by the heat of the sun and attains a higher temperature than the colder water at deeper levels. So, ocean thermal energy is derived from the sun.\ © In ocean thermal energy conversion plants, the warm surface water of the ocean is used to boil a volatile liquid such as ammonia or a chlorofluorocarbon. This produces high-pressure vapour, which is used to turn the turbine of a generator and produce electricity.\ (d) 20 degrees Celsius
Page No 150:
Question 43:
The gravitational pull of the moon causes the sea-water to rise periodically.\
(a) What name is given to the condition of the sea when its water is raised? (b) What name is given to the condition of the sea when its raised water recedes? (c) What name is given to the energy which can be harnessed from this natural phenomenon? (d) Draw labelled diagram to show how this energy can be harnessed to generate electricity.
Answer:
(a) The name 'high tide' is given to the condition of the sea when its water is raised.\ (b) The name 'low tide' is given to the condition of the sea when its raised water recedes.\ © The name of the form of energy that can be harnessed by this process is 'tidal energy'.\ (d)
Page No 150:
Question 44:
When the material A mined from the earth is heated strongly in an insufficient supply of air, it produces a solid fuel B which consists mainly of carbon. When another material C obtained from trees is heated in an insufficient supply of air, it produces another solid fuel D which also consists mainly of carbon. Name A, B, C and D
Answer:
A: Coal (mined from the earth) Coal is mined from the earth.\ B: Coke. It consists mainly of carbon.\ C: Wood. It is obtained from trees.\ D: Charcoal. It consists mainly of carbon.
Page No 150:
Question 45:
A certain form of energy which is not sourced directly or indirectly from the sun and does not cause any pollution is very easily converted into electricity. This form of energy is, however, not available everywhere. Moreover, it is technically very difficult and expensive to obtain it. Name the form of energy.
Answer:
It is geothermal energy, which is not derived directly or indirectly from the sun and does not cause any pollution. It can be converted into electricity. Also, geothermal energy is not available everywhere and is very difficult and expensive to obtain.
Page No 156:
Question 1:
What type of nuclear reaction is responsible for the liberation of energy:\
(a) in a nuclear reactor? (b) in the sun?
Answer:
(a) The nuclear fission of the heavy nucleus of a radioactive atom is responsible for the liberation of energy.\ (b) The nuclear fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei produces energy in the sun.
Page No 156:
Question 2:
Which product of the nuclear fission of uranium-235 is utilised to cause further fission of its nuclei?
Answer:
The neutrons produced in the nuclear fission cause further fission of the heavy nuclei, leading to a self-sustaining chain reaction.
Page No 156:
Question 3:
Which particles bring about the fission of uranium-235?
Answer:
The low-energy neutrons bring about the fission of uranium-235.
Page No 156:
Question 4:
State whether the fission of uranium-235 is caused by low energy neutrons or high energy neutrons.
Answer:
The fission of uranium-235 is caused by low-energy neutrons, which are also called slow-moving neutrons.
Page No 156:
Question 5:
Name the type of nuclear reaction which is involved in the working of:\
(a) a hydrogen bomb.\ (b) an atom bomb.
Answer:
(a) Nuclear fusion is involved in the working of a hydrogen bomb.\ (b) Nuclear fission is involved in the working of an atom bomb.
Page No 156:
Question 6:
Name the moderator used in a nuclear reactor.
Answer:
Graphite acts as a moderator by slowing down fast-moving neutrons in a nuclear reactor.
Page No 156:
Question 7:
Of what material are the control rods of a nuclear reactor made?
Answer:
The control rods of a nuclear reactor are made of chemical elements that are capable of absorbing many neutrons without fissioning themselves, such as boron, silver, indium and cadmium.
Page No 156:
Question 8:
What do you think is the purpose of the thick, concrete chamber surrounding the reactor of a nuclear power plant?
Answer:
The purpose of the thick, concrete chamber surrounding the reactor of a nuclear power plant is to absorb the dangerous nuclear radiation so as to protect the outside world.
Page No 157:
Question 26:
(a) What is a nuclear reactor? What is the fuel used in a nuclear reactor? (b) With the help of a labelled diagram, describe the working of a nuclear power plant.\ (c) How is the working nuclear reactor of a power plant shut down in an emergency? (d) Name five places in India where nuclear power plants are located.
Answer:
(a) A nuclear reactor is a device to harness nuclear energy (fission energy) in a controlled and economical way. The energy produced is used to generate electricity and to power ships.\ Uranium is used as a fuel in a nuclear reactor.\
(b)
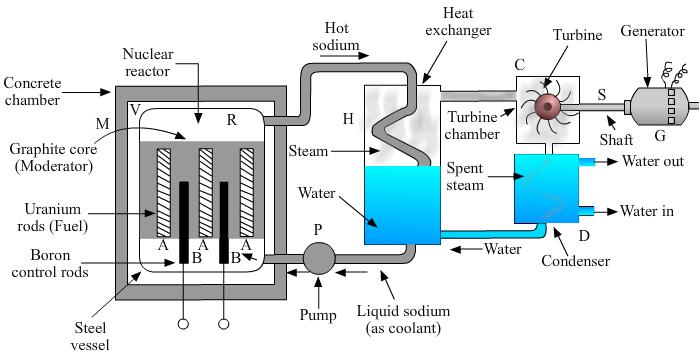
In a nuclear power plant, the fission of U-235 is carried out in a steel vessel (V) of the reactor. Enriched uranium rods (A) are inserted in a graphite core. Here, graphite acts as a moderator that slows down the speed of neutrons. Boron rods (B) are inserted between the uranium rods. These boron rods control the fission reaction. The controlled fission of U-235 produces a large amount of heat energy. Liquid sodium is pumped continuously through the pipes embedded in the reactor, and it absorbs the heat produced in the reactor. The extremely hot sodium is then passed into the coil of a heat exchanger (H) containing water. The water absorbs the heat from the sodium and boils to form steam. The steam thus formed at high pressure is introduced into a turbine chamber (C) with a turbine (T). The turbine rotates because of the pressure of the steam and drives the generator to produce electricity.\
© In case of an emergency, the control rods are fully inserted in the reactor. They absorb all the neutrons, shutting down the reactor.\
(d) Five places in India where nuclear power plants are located are the following.
1. Tarapur (Maharashtra) 2. Kalapakkam (Tamil Nadu) 3. Kakrapar (Gujarat) 4. Narora (Uttar Pradesh) 5. Kaiga ( Karnataka )
Page No 157:
Question 9:
Where, in a nuclear power station, is uranium used up?
Answer:
In a nuclear power station, uranium is used as a fuel to produce heat.
Page No 157:
Question 10:
State one use of nuclear fission reactions.
Answer:
The energy produced during nuclear fission reactions is used for generating electricity .
Page No 157:
Question 11:
Name the unit which is commonly used for expressing the energy released in nuclear reactions.
Answer:
The energy released in nuclear reactions is expressed in the unit of 'electron volt' (eV) or 'million electron volt' (MeV). The electron volt is a small unit, so the energy released in nuclear reactions is usually expressed in terms of million electron volts.
Page No 157:
Question 12:
How many MeV are equivalent to 1 atomic mass unit (u)?
Answer:
One atomic mass unit (u) is equivalent to 931 MeV of energy.
Page No 157:
Question 13:
Fill in the following blank with suitable words:\
(a) Splitting of a heavy nucleus into two lighter nuclei is called ……..\ (b) Uranium-235 atoms will split when hit by ………. This is called ………..\ (c) Nuclear ………. is used in nuclear power stations for the production of electricity.\ (d) In a nuclear power station, nuclear fission takes place in the ………….
Answer:
(a) Splitting of a heavy nucleus into two lighter nuclei is called nuclear fission .\ (b) Uranium-235 atoms will split when hit by neutrons. This is called nuclear fission .\ © Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations for the production of electricity.\ (d) In a nuclear power station, nuclear fission takes place in the reactor .
Page No 157:
Question 14:
What is nuclear fission? Explain with an example. Write the equation of the nuclear reaction involved.
Answer:
Nuclear fission Nuclear fission is the process by which the heavy nucleus of a radioactive atom splits up into smaller nuclei when bombarded with low-energy neutrons.\
Example:\ When uranium-235 atoms are bombarded with slow-moving neutrons, the heavy uranium nucleus breaks up to produce two medium-weight atoms, barium-139 and krypton-94, with the emission of three neutrons. A tremendous amount of energy is produced in this process.\ Reaction:\ U92238 + no1 −→−fission56Ba139+Kr9436+3n01+ Tremendous amount of energy
Page No 157:
Question 15:
(a) What is nuclear fusion? Explain with an example. Write the equation of the reaction involved.\ (b) Why are very high temperatures required for fusion to occur?
Answer:
(a) Nuclear fusion Nuclear fusion is the process by which two nuclei of light elements combine to form a heavy nucleus.\
Example:\ When deuterium atoms are heated to an extremely high temperature under extremely high pressure, two deuterium nuclei combine to form a heavy nucleus of helium, and a neutron is emitted. A tremendous amount of energy is liberated in this fusion reaction.\
Reaction:\ H12+H12→H23+n01+Tremendous amount of energy
(b) When two positively charged nuclei are brought together, they repel each other. Therefore, a very high temperature is required to force the lighter nuclei to fuse together to form a bigger nucleus.
Page No 157:
Question 16:
What is the nuclear fuel in the sun? Describe the process by which energy is released in the sun. Write the equation of the nuclear reaction involved.
Answer:
Hydrogen atoms can be considered a nuclear fuel in the sun because the sun derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen nuclei.\ The main nuclear fusion reaction taking place in the sun, a reaction that releases a tremendous amount of energy, is the fusion of four hydrogen atom nuclei to form the bigger nucleus of the helium atom. The total energy produced by the fusion of hydrogen into helium is tremendous. All this energy is released in the form of heat and light.\
4 H11 −→−−−−−−−inside the sunnuclear fusionHe2 4+ 2e10+Tremendous amount of energy
Page No 157:
Question 17:
(a) Write Einstein's mass-energy equation. Give the meaning of each symbol which occurs in it.\ (b) If 25 atomic mass units (u) of a radioactive material are destroyed in a nuclear reaction, how much energy is released in MeV?
Answer:
(a) Einstein's mass–energy equation is given as follows:\ E=mc2
E is the amount of energy produced if mass, m, is destroyed and c is the speed of light.
(b) If 25 atomic mass units (u) of a radioactive material is destroyed in a nuclear reaction, then the amount of energy released in MeV is given by:\ 25 ×
931 = 23275 MeV (since 1 u = 931 MeV)
Page No 157:
Question 18:
(a) What is the source of energy of the sun and other stars? (b) Describe the working of a hydrogen bomb.\ (c) What is common between the sun and a hydrogen bomb?
Answer:
(a) The sun and other stars obtain their energy from the nuclear fusion reactions of hydrogen. So, hydrogen can be considered a source of energy.\
(b) We know that a hydrogen bomb consists of deuterium, tritium and lithium. A hydrogen bomb is exploded by using an atom bomb. When an atom bomb is exploded, much heat is produced, which raises the temperature of deuterium and tritium to an extent in a small time. At this temperature, fusion reactions of deuterium and tritium take place, producing a tremendous amount of energy. This process causes the explosion of a hydrogen bomb, releasing an enormous amount of energy in a very short time.\
© In the sun as well as in a hydrogen bomb, energy is produced by nuclear fusion reactions of hydrogen.
Page No 157:
Question 19:
(a) What will happen if slow moving neutrons are made to strike the atoms of a heavy element U92235
? What is the name of this process? (b) Write a nuclear equation to represent the process which takes place.\ (c) Name one installation where such a process is utilised.
Answer:
(a) When the atoms of a heavy element, U-235, are bombarded with slow-moving neutrons, the uranium nucleus breaks up to produce two medium-weight atoms, barium-139 and krypton-94, with the emission of three neutrons. A tremendous amount of energy is produced in this process. The name of this process is nuclear fission.\
(b) The nuclear reaction is as follows.\
U92235 +n01 −→−fissionBa56139 +Kr3694 +3n01 +Tremendous amount of energy
© The process is used in nuclear power stations.\
U92235
Page No 157:
Question 20:
(a) What are the advantages of nuclear energy? (b) State the disadvantages of nuclear energy?
Answer:
(a) The advantages of nuclear energy are given below.\ 1. In the production of nuclear energy, gases such as carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide are not produced. So, it does not contribute to the greenhouse effect or acid rain.\ 2. There is no need for putting in nuclear fuel again and again, because once the fuel is loaded into the reactor, the nuclear power plant can go on producing electricity for two to three years at a stretch.\
(b) The disadvantages of nuclear energy are given below.\ 1. The waste products are radioactive, and they keep on emitting harmful radiations.\ 2. The availability of fuel is limited.\ 3. There is the risk of accidents in nuclear reactors, which may lead to the leakage of radioactive materials, causing serious damage to all living things.
Page No 157:
Question 21:
The following questions are about the nuclear reactor of a power plant.\
(a) Which isotope of uranium produces the energy in the fuel rods? (b) Will the fuel rods last for ever? (c) Is the energy produced by nuclear fission or nuclear fusion? (d) What is the purpose of using the graphite moderator? (e) What is the function of boron rods in the nuclear reactor? (f) Why is liquid sodium (or carbon dioxide gas) pumped through the reactor?
Answer:
(a) Uranium-235 produces the energy in the fuel rods.\ (b) No. But a nuclear power plant can work day and night for two to three years on the same uranium fuel.\ © Its energy is produced by nuclear fission.\ (d) Graphite acts a moderator in the reactor by slowing down fast-moving neutrons in it.\ (e) The boron rods act as control rods and absorb excess neutrons, preventing the fission reaction from going out of control.\ (f) Liquid sodium is pumped to transfer the heat produced in the reactor by fission to a heat exchanger for converting water into steam.
Page No 157:
Question 22:
In the reactor of a nuclear power plant, name the material which is used:\
(a) as a moderator\ (b) to absorb radiations\ (c) in the fuel rods\ (d) in the control rods\ (e) to carry away heat
Answer:
(a) Graphite is used as a moderator.\ (b) The reactor is enclosed in a concrete chamber to absorb the nuclear radiation.\ © Uranium-235 is used in the fuel rods.\ (d) Boron rods are used as the control rods.\ (e) Liquid sodium is used to carry away the heat.
Page No 157:
Question 23:
In the nuclear reactor of a power plant:\
(a) how do control rods control the rate of fission? (b) how is heat removed from the reactor core, and what use is made of this heat?
Answer:
(a) Control rods control the rate of fission by absorbing excess neutrons.\ (b) Liquid sodium is used to remove the heat from the reactor core. It is used as a coolant, and it transfers the heat to the heat exchanger. This heat is used to convert water into steam.
Page No 157:
Question 24:
How does inserting the control rods in the graphite core affect the fission in the reactor? Explain your answer.
Answer:
When the control rods are inserted in the graphite core, they absorb excess neutrons and thus prevent the fission reaction from going out of control.
Page No 157:
Question 25:
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using nuclear fuel for generating electricity?
Answer:
Advantages: 1. Nuclear power stations need less fuel than power stations that burn fossil fuels to produce the same amount of electricity.\ 2. There is no emission of greenhouse gases.\ 3. Nuclear fuel does not produce sulphur dioxide, a gas that affects health and produces acid rain.\
Disadvantages: 1. The initial cost of designing and building a nuclear power station is high.\ 2. Thermal pollution occurs because of the discharge of hot water from nuclear power stations.\ 3. There is the risk of accidents in a nuclear reaction.
Page No 158:
Question 27:
(a) Differentiate between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.\ (b) Which of the two, nuclear fusion and nuclear fusion, is made use of:\ (i) for the production of electricity? (ii) for making a hydrogen bomb? (c) Which produces more energy : nuclear fusion or nuclear fission? (d) Calculate the energy released in joules when 5 g of a material is completely converted into energy doing a nuclear reaction.\ (e) How much is this energy in MeV? (Speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s)
Answer:
↵(a) Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion can be differentiated as follows.
| Nuclear fission | Nuclear fusion | |
| Definition | Fission is the splitting of the heavy nucleus of a radioactive atom into smaller nuclei. | Fusion is the fusing of two or more lighter nuclei into a heavy nucleus. |
| Natural occurrence of the process | The process of nuclear fission does not normally occur in nature. | Fusion occurs in stars, such as the sun. |
| Energy released | The energy released by fission is a million times greater than that released in chemical reactions, but is lower than the energy released by nuclear fusion. | The energy released by fusion is three to four times greater than the energy released by fission. |
(b) (i) Nuclear fission can be used for the production of electricity.\ (ii) The process of nuclear fusion is used for making hydrogen bombs.\
© Nuclear fusion. The energy released by fusion is three to four times greater than the energy released by fission.\
(d) The energy released in joules when 5 g (5/1000 kg ) of a material is completely converted into energy during a nuclear reaction is given by Einstein's equation as
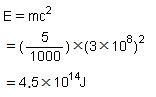
(e) The energy in MeV is given by:
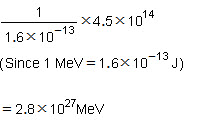
Page No 158:
Question 28:
Which of the following is used as a moderator in the reactor of a nuclear power station?
(a) liquid sodium\ (b) boron\ (c) graphite\ (d) carbon dioxide
Answer:
(c) graphite\
Graphite acts a moderator in the reactor by slowing down fast-moving neutrons in it.
Page No 158:
Question 29:
The control rods used in the reactor of a nuclear power plant are made of:\
(a) steel\ (b) graphite\ (c) uranium\ (d) boron
Answer:
(d) boron\
Boron is used in the control rods as it absorbs neutrons.
Page No 158:
Question 30:
The 'coolants' which can be used in the reactor of a nuclear power station are:\
(a) liquid mercury and nitrogen dioxide\ (b) liquid sodium and carbon dioxide\ (c) liquid ammonia and carbon monoxide\ (d) liquid boron and uranium oxide
Answer:
(b) liquid sodium and carbon dioxide\
Liquid sodium and carbon dioxide are used in order to transfer the heat produced in the reactor by fission to the heat exchanger, for converting water into steam.
Page No 158:
Question 31:
In a nuclear power plant, coolant is a substance:\
(a) which cools the hot, spent steam to condense it back to water\ (b) which transfers heat from reactor to water in heat exchanger\ (c) which is boiled to make steam to turn the turbine\ (d) which cools the generator coils to prevent their overheating.
Answer:
(b) which transfers the heat from the reactor to the water in the heat exchanger\
Liquid sodium or carbon dioxide gas is used as a coolant.
Page No 158:
Question 32:
Which of the following is ultimately not derived from the sun's energy (or solar energy)?
(a) wind energy\ (b) nuclear energy\ (c) biomass energy\ (d) ocean thermal energy
Answer:
(b) nuclear energy\
Nuclear energy comes from the nucleus of an atom.
Page No 158:
Question 33:
One atomic mass unit (u) is equivalent to an energy of:\
(a) 931 eV\ (b) 9.31 MeV\ (c) 1 MeV\ (d) 931 MeV
Answer:
(d) 931 MeV\
One atomic mass unit is equal to 931 MeV.
Page No 158:
Question 34:
The energy in the reactor of a nuclear power station is produced by the process of:\
(a) nuclear diffusion\ (b) nuclear fission\ (c) nuclear fusion\ (d) nuclear fermentation
Answer:
(b) nuclear fission\
In a nuclear reactor, the controlled fission of uranium-235 produces a large amount of heat energy.
Page No 158:
Question 35:
One eV (electron volt) of nuclear energy is equivalent of:\
(a) 1.6 × 10−14 J\ (b) 1.6 × 10−12 J\ (c) 1.6 × 10−19 J\ (d) 1.6 × 10−13 J
Answer:
(c) 1.6 × 10−19 J\
It is the amount of energy acquired by an electron having a charge of 1.6 × 10−19 C when accelerated through a potential difference of 1 volt.
Page No 158:
Question 36:
Which of the following can be produced during the nuclear fission as well as nuclear fusion reactions?
(a) protons\ (b) deutrons\ (c) electrons\ (d) neutrons
Answer:
(d) neutrons\
In both reactions, neutrons can be produced.
Page No 158:
Question 37:
Nuclear fission reactions are not a source of energy for one of the following. This is:\
(a) atom bomb\ (b) power plants\ (c) sun\ (d) pacemaker
Answer:
(c) sun\
Nuclear fusion reactions are the source of the sun's energy.
Page No 158:
Question 38:
The energy produced by converting 1 gram mass of a nuclear fuel into energy completely is:\
(a) 9 × 1016 J\ (b) 9 × 1014 J\ (c) 9 × 1015 J\ (d) 9 × 1013 J
Answer:
(d) 9 × 1013 J\
The energy produced by converting 1 gram (1/1000 kg) mass of a nuclear fuel is given by Einstein's equation as\
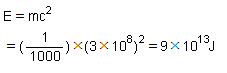
Page No 158:
Question 39:
The source of energy of the sun is:
(a) conversion of hydrogen gas into helium (b) conversion of carbon fuel into carbon dioxide (c) burning of hydrogen gas present in the sun (d) disintegration of uranium into barium and krypton
Answer:
(a) conversion of hydrogen gas into helium
The sun's energy is derived from the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei.
Page No 158:
Question 40:
An uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction forms the basis of:
(a) nuclear power plant (b) hydrogen bomb (c) thermal power station (d) atom bomb
Answer:
(d) atom bomb
In an atom bomb, the fission reaction of uranium-235 or plutonium-239 is deliberately allowed to go out of control so as to produce an enormous amount of energy in a very short time.
Page No 158:
Question 41:
One MeV of nuclear energy is equivalent to:
(a) 1.6 × 10−13 J (b) 1.6 × 10−19 J (c) 1.6 × 10−16 J (d) 1.6 × 10−15 J
Answer:
(a) 1.6 × 10−13 J
One MeV of nuclear energy is equal to 1.6 × 10-13 J.
Page No 158:
Question 42:
One type of energy which has not been controlled so far is:
(a) ocean thermal energy (b) nuclear fusion energy (c) geothermal energy (d) nuclear fission energy
Answer:
(b) nuclear fusion energy
The energy produced in a nuclear fusion reaction is much more than that produced in a nuclear fission reaction and has not been controlled so far.
Page No 159:
Question 43:
The disposal of wastes produced in a nuclear power plant poses a big problem because it is:
(a) too heavy (b) highly inflammable (c) extremely foul smelling (d) highly radioactive
Answer:
(d) highly radioactive
The waste materials produced by the fission of uranium-235 in a nuclear power plant are radioactive and hence extremely harmful to all living things.
Page No 159:
Question 44:
The heat energy released during nuclear fission and fusion is due to the:
(a) conversion of stored chemicals into energy (b) conversion of momentum into energy (c) conversion of mass into energy (d) conversion of magnetism into energy
Answer:
(c) conversion of mass into energy
In both the reactions, heat energy is released owing to the conversion of mass into energy.
Page No 159:
Question 45:
Which of the following can undergo nuclear fusion reaction?
(a) uranium (b) deuterium (c) barium (d) krypton
Answer:
(b) deuterium
In nuclear fusion, two nuclei of light elements such as that of hydrogen are combined to form a heavy nucleus. Deuterium atoms are the hydrogen atoms of mass number 2.
Page No 159:
Question 46:
A nuclear reaction is represented by the following equation: U92235 + n01 −→−−−− Ba56139 + Kr3694 + xc + E
(a) Name the process represented by this equation and describe what takes place in this reaction (b) Identify the particle c and the number x of such particles produced in the reaction. (c) What does E represent? (d) Name one installation where the above nuclear reaction is utilised. (e) What type of bomb is based on similar type of reaction?
Answer:
(a) The process represents nuclear fission. In this process, a heavy nucleus of uranium splits into two smaller nuclei of barium and krypton when bombarded with low-energy neutrons. A tremendous amount of energy is also produced. (b) Particle c is a neutron and x is equal to 3. © E represents the tremendous amount of energy that is liberated in the reaction. (d) The given reaction is utilised in nuclear power stations. (e) An atom bomb is based on a similar type of reaction.
Page No 159:
Question 47:
A nuclear reaction is represented by the equation: H12 + H12 −→−−−− He23 + xc + E
(a) Name the process represented by this equation and describe what happens during this reaction. (b) Identify the particle c and the number x of such particles produced in the reaction. (c) What does E represent? (d) State two conditions under which such a reaction takes place. (e) What type of nuclear bomb is based on similar reactions?
Answer:
(a) The process represents nuclear fusion. In this process, when two smaller nuclei of deuterium are heated to an extremely high temperature under extremely high pressure, a heavy nucleus of helium and a neutron are emitted. A tremendous amount of energy is also liberated. (b) Particle c is a neutron and x is equal to 1. © E represents the tremendous amount of energy liberated. (d) The two conditions are given below. (i) Millions of degrees of temperature (ii) Millions of pascals of pressure (e) A hydrogen bomb is based on similar reactions.
Page No 159:
Question 48:
The mass numbers of four elements A, B, C and D are 2, 20, 135 and 235, respectively. Which one of them will be most suitable to make: (i) an atom bomb, and (ii) a hydrogen bomb?
Answer:
(i) An atom bomb is based on nuclear fission reactions. So, a heavy nucleus D of mass number 235 is the most suitable to make it. (ii) A hydrogen bomb is based on nuclear fusion reactions. So, a light element A of mass number 2 is the most suitable to make it.
Page No 159:
Question 49:
A nuclear power plant is working normally. What would you do if the reactor core suddenly got too hot?
Answer:
If the reactor core suddenly gets very hot, then we should insert the control rods of boron a little further into the reactor to reduce the rate of the nuclear fission reaction.
Page No 159:
Question 50:
A nuclear reactor has half the length of all its control rods inserted in graphite. What must be done so that the reactor produces more heat? Explain your answer.
Answer:
The control rods should be withdrawn a little more from the inside of the nuclear reactor to increase the rate of the nuclear fission reaction and produce more heat.
Page No 159:
Question 51:
Explain why, in a nuclear reactor, the chain reaction stops if the control rods are fully inserted into the graphite.
Answer:
If the control rods are fully inserted into the graphite, they absorb all the neutrons and therefore the nuclear chain reaction stops.
Page No 161:
Question 9:
The major cause of environmental pollution is the use of:
(a) hydrogen as fuel (b) biomass energy (c) ocean energy (d) fossil fuels
Answer:
(d) fossil fuels
The burning of fossil fuels produces acidic gases and large amounts of carbon dioxide and smoke, all of which pollute the environment.
Page No 161:
Question 10:
The world's known coal reserves are expected to last for about:
(a) 200 years (b) 400 years (c) 500 years (d) 100 years
Answer:
(a) 200 years
The world's known coal reserves are expected to last for about 200 years.
Page No 161:
Question 11:
The fossil fuel whose known reserves in the earth are expected to last for the minimum period is:
(a) coal (b) uranium (c) petroleum (d) natural gas
Answer:
(c) petroleum
The known reserves of petroleum are expected to last for about 40 years.
Page No 161:
Question 12:
An energy efficient device for producing light is:
(a) DLF (b) CFL (c) FCL (d) LPG
Answer:
(b) CFL
A compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) is an energy-efficient device. It consumes much less electrical energy than other devices that provide light.
Page No 161:
Question 1:
Which of the two is a cleaner fuel: hydrogen or CNG? Why?
Answer:
Hydrogen is a cleaner fuel than CNG. This is because the burning of hydrogen produces only water, which is harmless. However, the burning of CNG gives water and carbon dioxide, a gas that can produce the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere, harming the environment.
Page No 161:
Question 2:
Which of the two is more energy efficient: filament type electric bulb or CFL? Why?
Answer:
A compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) is more energy efficient, because it consumes much less electrical energy than a filament-type electric bulb.
Page No 161:
Question 3:
How long are the energy resources of the earth like coal, petroleum and natural gas expected to last?
Answer:
The amounts of coal, petroleum and natural gas left in the earth are limited. It has been estimated that the world's coal reserves may last for another 200 years, the known reserves of petroleum for around 40 years and the known reserves of natural gas for around 60 years.
Page No 161:
Question 4:
Name two devices which can be utilised for the cooking of food so as to save fuel.
Answer:
Two devices that can be utilised for cooking food so as to save fuel are the following. 1. Solar cooker 2. Pressure cooker
Page No 161:
Question 5:
What are the various factors which we should keep in mind while choosing a source of energy?
Answer:
The following are the various factors that we should keep in mind while choosing a source of energy. 1. The ease of extracting energy from the source. 2. The cost of extracting energy from the source. 3. The efficiency of technology used in the extraction. 4. The effect of the energy source on the environment.
Page No 161:
Question 6:
Can any source of energy be pollution free? Explain your answer with an example.
Answer:
No source of energy can be pollution free. For example, solar cells, solar cookers and wind generators used for generating energy are pollution free, but the processes involved in making the materials to build these devices damage the environment in some way.
Page No 161:
Question 7:
What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy?
Answer:
The following are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy. 1. More nuclear power plants are being set up, increasing the radioactivity in the environment. 2. The ecological balance is being disturbed by the construction of hydropower plants. 3. The amount of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increasing because of the burning of fossil fuels. 4. The combustion of fossil fuels is producing acid rain and damaging plants, soil and aquatic life.
Page No 161:
Question 8:
What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption?
Answer:
The following are a few steps to reduce energy consumption. 1. Switch off electrical devices such as TV, lights and fans when they are not needed. 2. Use energy-efficient electrical appliances. 3. Use pressure cookers and solar cookers for cooking food. 4. Use solar water heaters. 5. Encourage the use of biogas as a fuel in rural areas.