Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur (Physics) Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 - Sources Of Energy Part 1
Part 1
Question 1:
Name a non-renewable source of energy other than fossil fuels.
Answer:
Nuclear fuel, such as uranium, is a non-renewable source of energy other than fossil fuels.
Page No 121:
Question 2:
Define calorific value of a fuel.
Answer:
The amount of heat produced when a unit mass of a fuel is completely burnt is known as the calorific value of the fuel.
Page No 121:
Question 3:
“The calorific value of cooking gas (LPG) is 50 kJ/g”. What does it mean?
Answer:
When you say that the caloric value of cooking gas (liquefied petroleum gas, or LPG) is 50 kJ/g, it means that when 1 gram of LPG is burnt completely, it produces 50 kilojoules of energy in the form of heat.
Page No 121:
Question 4:
Which of the following produces more heat (per unit mass) on burning? Coal or LPG
Answer:
Liquefied petroleum gas, or LPG, produces more heat than coal, because LPG (50 kJ/g) has higher a calorific value than coal (25-30 kJ/g).
Page No 122:
Question 18:
(a) What is a fuel? Give five examples of fuels. (b) What are the characteristics of an ideal fuel (or good fuel)? (c) The calorific value and ignition temperature of fuel A are 55 kJ/g and 80°C, respectively. These values for fuel B are 80 kJ/g and 10°C, respectively. On burning, the fuel A produces CO2 and H2 O while the fuel B produces CO2 , CO and SO2. Give three points of relative advantages and disadvantages of these two fuels.
Answer:
a) Materials that burn to produce heat energy are known as fuels. Examples of fuels are wood, coal, petrol, diesel and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
b) The characteristics of a good fuel are the following. 1. It should have a high calorific value, i.e., it should give an adequate amount of heat per unit mass. 2. It should burn without giving out any harmful gases, so that it does not pollute the air. 3. It should have a proper ignition temperature, so that it burns easily. (Its ignition temperature should neither be too low nor too high.) 4. It should be cheap, easily available and easy to handle. 5. After burning, it should not leave much ash.
c) Advantages of fuel 'A'. 1.It has a moderate ignition temperature. 2. It does not produce any harmful gases.
Disadvantage: 1. It has a low calorific value and produces less heat per unit mass.
Advantage of fuel 'B': 1. It has a high calorific value and hence generates more heat.
Disadvantages: 1. It has a very low ignition temperature and hence is unsafe to use. 2. It produces harmful gases, such as CO and SO2 .
Page No 122:
Question 19:
An examples of a renewable source of energy is:
(a) petrol (b) natural gas (c) biogas (d) kerosene
Answer:
© Biogas
Biogas is a renewable source of energy .
Page No 122:
Question 20:
A non-renewable source of energy is:
(a) wood (b) alcohol (c) hydrogen gas (d) natural gas
Answer:
(d) natural gas
Natural gas is a non-renewable source of energy as it takes thousands of years to form.
Page No 122:
Question 21:
Which of the following is not a renewable source of energy?
(a) wind (b) flowing water (c) fossil fuels (d) fuel wood
Answer:
© Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy because they are present in limited amounts on the earth.
Page No 122:
Question 22:
A good fuel is one which possesses:
(a) high calorific value and low ignition temperature (b) high calorific value and high ignition temperature (c) high calorific value and moderate ignition temperature (d) low calorific value and moderate ignition temperature
Answer:
© high calorific value and moderate ignition temperature
A good fuel should have a high calorific value so that it can give us more heat per unit mass. It should also have a moderate ignition temperature.
Page No 122:
Question 23:
The fuel having a calorific value of 55 kJ/g is likely to be:
(a) biogas (b) methane gas (c) hydrogen gas (d) natural gas
Answer:
(b) methane gas
Methane has a calorific value of 55 kJ/g.
Page No 122:
Question 24:
A newly planted sapling usually grows and matures into a tree in more than:
(a) 50 years (b) 25 years (c) 45 years (d) 15 years
Answer:
(d) 15 years
A plant sapling takes more than 15 years to grow and mature into a tree.
Page No 122:
Question 25:
Which of the following fuels has the highest calorific value?
(a) natural gas (b) methane gas (c) hydrogen gas (d) biogas
Answer:
© Hydrogen gas
Hydrogen gas has the highest calorific value (150 kJ/g).
Page No 122:
Question 26:
The fuel having the lowest calorific value is:
(a) coal (b) wood (c) charcoal (d) kerosene
Answer:
(b) wood
Wood has the lowest calorific value among the given fuels.
Page No 122:
Question 5:
Define ignition temperature of a fuel.
Answer:
The ignition temperature of a fuel is the minimum temperature to which a fuel must be heated so that it catches fire and starts burning.
Page No 122:
Question 6:
“The ignition temperature of a fuel is 80°C”. What does this mean?
Answer:
If the ignition temperature of a fuel is 80°C, it means that the fuel must be heated up to 80°C to burn. No fuel can burn unless it is heated to its ignition temperature.
Page No 122:
Question 7:
Fill in the following blank with a suitable word: The amount of heat produce by burning a unit mass of a fuel completely is known as its ………… value.
Answer:
The amount of heat produced by burning a unit mass of a fuel completely is known as its 'calorific' value.
Page No 122:
Question 8:
What is a source of energy? What are the two main categories of the sources of energy?
Answer:
A source of energy is that which provides a required amount of energy in a convenient form for a long time. There are basically two types of sources of energy: a) Renewable source of energy b) Non-renewable source of energy
Page No 122:
Question 9:
State any four characteristics of a good source of energy.
Answer:
Four characteristics of a good source of energy are as follows. a) It should have a high calorific value. b) It should be cheap and easily available. c) It should be safe to handle and use. d) It should be environment friendly, i.e, it should not cause pollution.
Page No 122:
Question 10:
What is meant by a non-renewable source of energy? Give two examples of non-renewable source of energy.
Answer:
The sources of energy that have accumulated in nature over a very long time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted are called non-renewable sources of energy.
The two examples of non-renewable sources of energy are: a) Fossil fuels (such as coal, petroleum and natural gas) b) Nuclear fuels (such as uranium)
Page No 122:
Question 11:
What is meant by a renewable source of energy? Give two examples of renewable sources of energy.
Answer:
The sources of energy that are being produced continuously in nature and are inexhaustible are called renewable sources of energy. Examples: Wind, wood, sunlight and biomass.
Page No 122:
Question 12:
What is the difference between a renewable and a non-renewable source of energy? Explain with examples.
Answer:
| Renewable Sources of Energy | Non-Renewable Sources of Energy |
1. Renewable sources of energy are those sources of energy that are being produced continuously in nature. 2.These sources of energy can be used again and again. 3. Examples of renewable sources of energy are wind, sunlight and tides. |
Non-renewable sources of energy are those sources of energy that have accumulated in nature over a very long time. These sources of energy cannot be used again and again. Examples of non-renewable sources of energy are coal, petroleum and natural gas. |
Page No 122:
Question 13:
Why are fossil fuels classified as non-renewable source of energy?
Answer:
Fossil fuels are classified as non-renewable sources of energy because they are present in limited amounts on the earth. Once they are exhausted, they cannot be replenished, and they will no longer be available to us.
Page No 122:
Question 14:
Name two sources of energy that you think are renewable. Give reason for your choice.
Answer:
The following are two sources of energy that are renewable. a) Wind, which is used to generate energy using wind turbines b) Water, which is used to generate hydroelectricity from flowing water They are renewable because they are abundant in nature and can be used again and again..
Page No 122:
Question 15:
Name two sources of energy which you consider to be non-renewable. Give reason for your choice.
Answer:
The following are two non-renewable sources of energy. a) Coal b) Crude oil They are non-renewable because they are present in limited amounts on the earth. Once they are exhausted, they cannot be replenished, and they will no longer be available to us.
Page No 122:
Question 16:
(a) Classify the following into renewable and non-renewable sources of energy: Coal, Wind, Tides, Petroleum,Wood, Natural gas (b) What is the basis of above classification?
Answer:
(a) Coal, petroleum and natural gas are non-renewable sources of energy, whereas wind, tides and wood are renewable sources of energy. (b) The basis of the above classification is the abundance or depletion of the energy sources mentioned and the amount available for the future.
Page No 122:
Question 17:
Coal is said to be formed from the wood of trees. Why then is coal considered to be a non-renewable source of energy whereas wood is a renewable source of energy?
Answer:
Coal is classified as a non-renewable source of energy because, when trees die and are buried in the earth, they take many years to decompose and form coal. So, they are not easily available. But wood will continue to be available to us if we use it properly as per a plan.
Page No 123:
Question 27:
There are four fuels which all contain only carbon and hydrogen. The fuel having highest calorific value will be one which has:
(a) more of carbon but less of hydrogen (b) less of carbon but more of hydrogen (c) equal proportions of carbon and hydrogen (d) less of carbon as well as less of hydrogen
Answer:
(b) less of carbon but more of hydrogen gas
The fuel with the highest calorific value would have less carbon and more hydrogen, because hydrogen has a higher calorific value than carbon.
Page No 123:
Question 28:
One of the following is not a characteristic of a good fuel. This is:
(a) high calorific value (b) no emission of smoke (c) smooth burning (d) high ignition temperature
Answer:
(d) high ignition temperature
A good fuel should not have a high ignition temperature.
Page No 123:
Question 29:
Which of the following is not a fossil fuel?
(a) coal (b) petroleum gas (c) biogas (d) natural gas
Answer:
© Biogas
Fossils form deep under the earth's surface from the prehistoric remains of living organisms. Biogas is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide. It is produced by the anaerobic degradation of animal wastes such as cow dung in the presence of water.
Page No 123:
Question 30:
The calorific values of three fuels A, B and C are 33 kJ/g, 48 kJ/g and 150 kJ/g, respectively. A is solid, B is liquid and C is a gas at room temperature. One combustion, both A and B produce carbon dioxide while C explodes forming steam. B and C leave no residue after combustion while A leaves behind some solid residue. Which one of the three fuels is the most ideal? Give two reasons to support your answer.
Answer:
Fuel A has a low calorific value compared with the other fuels, and therefore, it cannot be considered the most ideal fuel.
Fuel B is the most ideal fuel of the three for the following reasons. (a) It has a high calorific value. (b) It burns completely without leaving any residue.
Fuel C has both the characteristics of fuel B but is unsafe as it explodes.
Hence, B is the ideal fuel.
Page No 123:
Question 31:
Calorific value and ignition temperature of fuel X are 75 kJ/g and 20°C respectively. These values for fuel Y are 50 kj/g and 75°C respectively. On burning, the fuel Y produces only CO2 while fuel X produces CO2 and CO. Which of the two is a better fuel? Give two reasons to support your answer.
Answer:
Fuel Y is the better fuel for the following reasons. (a) It has a moderate ignition temperature of 75°C, i.e., neither too high nor too low. (b) It does not produce harmful gases such as carbon monoxide (CO).
Page No 123:
Question 32:
The calorific values of five fuels A, B, C, D and E are given below:
| A | 48 kJ/g | |
| B | 17 kJ/g | |
| C | 150 kJ/g | |
| D | 50 kJ/g | |
| E | 30 kJ/g |
Which of the fuels could be : (i) cooking gas (ii) alcohol (iii) wood (iv)hydrogen (v) kerosene?
Answer:
(i) Cooking gas is D. (ii) Alcohol is E. (iii) Wood is B. (iv) Hydrogen gas is C. (v) Kerosene is A.
Page No 123:
Question 33:
Arrange the following fuels in the order of decreasing calorific values (keeping the fuel with highest calorific value first): Biogas, Kerosene, Wood, Petrol, Hydrogen gas, Methane
Answer:
The fuels in the decreasing order of calorific values are as follows.
Hydrogen gas (150 kJ/g) > Methane (55 kJ/g) > Petrol (50 kJ/g) > Kerosene (48 kJ/g) > Biogas (40 kJ/g) > Wood (17 kJ/g)
Page No 123:
Question 34:
Arrange the following fuels in the order of increasing calorific values (keeping the fuel with lowest calorific value first): LPG, Coal, Alcohol, Dung cakes, Diesel
Answer:
The fuels in the increasing order of calorific values are as follows. Dung cakes < Coal < Alcohol < Diesel < LPG
Page No 123:
Question 35:
Most of the fuels contain carbon as one of the constituents. Name a fuel which has very high calorific value but not contain carbon.
Answer:
Hydrogen gas has a high calorific value (150 kJ/g) but does not contain carbon.
Page No 130:
Question 1:
Name the product of petroleum that is used to drive heavy vehicles.
Answer:
Diesel is used to drive heavy vehicles.
Page No 130:
Question 2:
Give one example of a good domestic fuel.
Answer:
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is used as a domestic fuel.
Page No 130:
Question 3:
Name any one hydrocarbon fraction obtained during the fractional distillation of petroleum which is used as a domestic fuel.
Answer:
Kerosene is obtained during the fractional distillation of petroleum.
Page No 130:
Question 4:
What are the various fuels which are used to generate electricity in a thermal power plant?
Answer:
Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and gas, are burnt to generate electricity in a thermal power plant.
Page No 130:
Question 5:
Name any four fractions obtained from petroleum which are used as fuels.
Answer:
Four fractions obtained from petroleum that are used as fuels are petrol (gasoline), diesel, kerosene and petroleum gas.
Page No 131:
Question 24:
(a) What are fossil fuels? Give three examples of fossil fuels. (b) Describe how fossil fuels were formed. (c) Explain how, sun is considered to be the ultimate source of fossil fuels. (d) Which fossil fuels were formed by the buried remains of small plants and animals? (e) Which fossil fuel formed by the buried remains of large land plants?
Answer:
(a) Natural fuels that are found deep inside the earth and are formed from the prehistoric remains of organisms are called fossil fuels. Three examples of fossil fuels are coal, petroleum and natural gas.
(b) Plants and animals that died millions of years ago got buried deep inside the earth and covered by mud and sand. In the absence of oxygen and because of the chemical effects of pressure, heat and bacteria, the remains of the plants and animals were, over the years, converted into fossil fuels, such as coal, petroleum and natural gas. The buried remains of large plants got converted into coal and those of small plants and animals into petroleum and natural gas.
© We know that green plants use sunlight for photosynthesis, which is the process by which they produce food for their growth. When animals eat plants for energy, they consume food made with the help of sunlight. When plants and animals die, their remains, which consist of material directly or indirectly made with the help of sunlight, are buried in the earth and converted into fossil fuels, such as coal and petroleum. Hence, the sun is the ultimate source of fossil fuels.
(d) Petroleum and natural gas are formed from the buried remains of small plants and animals.
(e) Coal is formed from the buried remains of large plants.
Page No 131:
Question 25:
The main constituent of petroleum gas is:
(a) methane (b) ethane (c) butane (d) propane
Answer:
© butane
Butane is the main constituent of petroleum gas.
Page No 131:
Question 26:
The natural gas consists mainly of:
(a) methane (b) ethane (c) propane (d) butane
Answer:
(a) methane
Natural gas consists mainly of methane.
Page No 131:
Question 27:
Which of the following is not produced by the burning of fossil fuels?
(a) nitrogen oxides (b) sulphur oxides (c) sodium oxides (d) carbon oxides
Answer:
© sodium oxides
The burning of fossil fuels produces sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and carbon dioxide.
Page No 131:
Question 28:
The product of petroleum used to drive heavy vehicles like trucks is:
(a) petrol (b) kerosene (c) diesel (d) petroleum gas
Answer:
© Diesel
Diesel is used to drive heavy vehicles.
Page No 131:
Question 29:
The aviation fuel which is used in the engines of jet aeroplanes is:
(a) diesel (b) kerosene (c) petrol (d) CNG
Answer:
(b) kerosene
A special grade of kerosene oil is used as aviation fuel in jet aeroplanes.
Page No 131:
Question 30:
The ultimate source of energy stored in fossil fuels is:
(a) moon (b) earth (c) sun (d) sea
Answer:
© sun
The sun is the ultimate source of energy stored in all fossil fuels.
Page No 131:
Question 31:
Which of the following is not a fossil source of energy?
(a) kerosene oil (b) cow-dung cakes (c) CNG (d) coal
Answer:
(b) Cow-dung cakes
Fossil fuels take thousands of years to form deep under the earth. Cow dung does not come under this category of fuels.
Page No 131:
Question 32:
The fuel which is not used at thermal power plants is:
(a) coal (b) uranium (c) natural gas (d) fuel oil
Answer:
(b) uranium
Thermal power plants use only coal, oil or gas as fuel.
Page No 131:
Question 6:
What is the composition of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)?
Answer:
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) consists mainly of butane along with smaller amounts of propane and ethane.
Page No 131:
Question 7:
Which gaseous fuel is being used increasingly in transport vehicles like cars and buses these days?
Answer:
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is being increasingly used in transport vehicles.
Page No 131:
Question 8:
Write the full form of: (i) LPG, and (ii) CNG.
Answer:
The full forms of the abbreviations LPG and CNG are as follows. (i) LPG is liquefied petroleum gas. (ii) CNG is compressed natural gas.
Page No 131:
Question 9:
What is the main constituent of:
(i) petroleum gas? (ii) natural gas?
Answer:
The main constituents of these gases are as follows. (i) Petroleum gas: Butane (ii) Natural gas: Methane
Page No 131:
Question 10:
Name the component which is found in natural gas well as in biogas.
Answer:
Methane is found in natural gas as well as in biogas.
Page No 131:
Question 11:
State two important uses of natural gas.
Answer:
Two uses of natural gas are a) as a fuel in thermal power plants b) as a fuel in transport vehicles
Page No 131:
Question 12:
State one important use of CNG these days.
Answer:
Compressed natural gas (CNG ) is used as a fuel for transport vehicles.
Page No 131:
Question 13:
Complete the following sentence: Domestic gas cylinders like Indane contain mainly …………..
Answer:
Domestic gas cylinders, such as those of Indane, mainly contain 'butane'.
Page No 131:
Question 14:
Explain why, natural gas is considered to be a good fuel.
Answer:
Natural gas is a good fuel because it has a high calorific value of up to 50 kJ/g. It burns with a smokeless flame and causes no air pollution. There is also no need for additional storage and transport because it can be directly supplied from gas wells to homes.
Page No 131:
Question 15:
What is meant by conventional sources of energy? Write the names of two conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
The traditional sources of energy that are familiar to most people are called conventional sources of energy. Coal and petroleum are two conventional sources of energy.
Page No 131:
Question 16:
Explain the principle of working of a thermal power plant. Draw labelled diagram to illustrate your answer.
Answer:
A diagram showing the working of a thermal power plant:
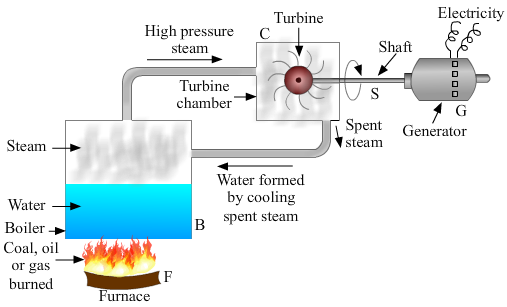
Explanation: In a thermal power plant, electricity is generated using coal as the fuel. Coal is used to generate steam, which helps rotate turbines connected to a generator. The generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Page No 131:
Question 17:
What are the disadvantages of burning fossil fuels?
Answer:
The disadvantages of burning fossil fuels are as follows. (a) The burning of fossil fuels produces gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which cause acid rain, damaging trees and land and affecting aquatic life. (b) It produces carbon dioxide, which affects all kinds of organisms. © It produces smoke and ashes, which cause air pollution.
Page No 131:
Question 18:
Write a short note on the pollution caused by burning fossil fuels.
Answer:
The burning of fossil fuels produces gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides that cause acid rain. Acid rain damages trees, land and buildings and affects aquatic life. The burning of fossil fuels produces carbon dioxide, which is responsible for the greenhouse effect on the earth. It also produces smoke and ashes, which pollute the air.
Page No 131:
Question 19:
What are the various steps which can be taken to control (or reduce) pollution caused by burning fossil fuels?
Answer:
Various steps can be taken to reduce the pollution caused by burning fossil fuels. These are as follows. (a) The air pollution caused by the burning of petroleum fuels in vehicles can be reduced by using catalytic converters in vehicles. Catalytic converters convert harmful gases into harmless gases. (b) The air pollution caused by the burning of coal in thermal power plants can be reduced by washing smoke and acidic gases with water in scrubbers. © The air pollution caused by thermal power plants can also be reduced by installing electrostatic precipitators in their chimneys. The unburnt carbon particles and fly ash get deposited in the chimneys before the exhaust gases from the power plants are let into the air.
Page No 131:
Question 20:
If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Answer:
Natural gas can be used for heating and cooking food as it is a clean source of energy. It has a high calorific value and does not produce a large amount of smoke on burning. It is easy to use and transport.
Page No 131:
Question 21:
Why is LPG considered a good fuel?
Answer:
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is considered a good fuel for the following reasons. a) It has a high calorific value (50 kJ/g). b) It burns with a smokeless flame and hence does not pollute the air. c) It is easy to handle and convenient to store. d) It is a clean domestic fuel and does not produce any harmful gas.
Page No 131:
Question 22:
Why is LPG considered a better fuel than coal?
Answer:
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is considered a better fuel than coal for the following reasons. a) It has a higher calorific value (50 kJ/g) than coal (30 kJ/g). b) It burns with a smokeless flame and hence does not pollute air, whereas coal produces smoke on burning. c) It is easier to handle and more convenient to store than coal. d) It is a clean domestic fuel and does not produce any harmful gas, whereas coal, on burning, produces carbon dioxide, which causes air pollution.
Page No 131:
Question 23:
Why is the leakage of LPG detected easily although it is odourless? State the steps to be taken in case its leakage is detected in the kitchen.
Answer:
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is odourless, but to detect leakage of the gas, a small quantity of strong-smelling ethyl mercaptan (C2 H5 SH) is added to it. Ethyl mercaptan has a foul smell resembling that of hydrogen sulphide gas, which can be easily detected.
The following steps are to be taken when leakage of LPG is detected in the kitchen. a) Lighted matchsticks and other burning substances should be kept away. b) The knob of the gas stove must be closed. c) The valve of the gas cylinder should be checked and changed immediately if any damage is found.
Page No 132:
Question 33:
LPG consists mainly of:
(a) butane (b) ethane (c) butanone (d) methane
Answer:
(a) butane
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) consists mainly of butane, along with smaller amounts of propane and ethane.
Page No 132:
Question 34:
Coke is move valuable when used:
(a) as a fuel for industrial boilers (b) as an oxidising agent (c) as a reducing agent (d) as a fuel in domestic ovens
Answer:
© as a reducing agent
Coke is used as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals from their ores.
Page No 132:
Question 35:
Coal cannot be converted into one of the following forms of energy. This is:
(a) coal gas (b) electricity (c) oil (d) charcoal
Answer:
(d) charcoal
Charcoal cannot be obtained from coal.
Page No 132:
Question 36:
One of the following does not contribute to acid rain. That is:
(a) nitrogen monoxide (b) sulphur dioxide (c) carbon monoxide (d) carbon dioxide
Answer:
© carbon monoxide
Only nitrogen oxides, sulphur dioxide and carbon dioxide are responsible for acid rain.
Page No 132:
Question 37:
Fossil fuels are energy rich compounds of an element X which were originally made by the plants with the help of sun's energy.
(a) Name the element X. (b) Name another element which is usually found in combination with X in fossil fuels.
Answer:
(a) Element X is carbon. (b) Another element found in combination with carbon in fossil fuels is hydrogen.
Page No 132:
Question 38:
The energy in petrol originally came from the sun. Explain how it got into petrol.
Answer:
We know that green plants use the energy from sunlight for photosynthesis and growth. They store this energy in the form of carbon compounds. Thus, every leaf and every bit of wood in plants and trees is made using the energy from sunlight. Animals eat plants for energy, which is originally received from sunlight. These plants and animals die and their remains get converted into coal and petrol, respectively, which are energy-rich compounds of carbon that were made by plants using solar energy.
Page No 132:
Question 39:
A substance X is added to LPG cylinders while filling so as to make the detection of leakage of LPG from the cylinder easy.
(a) Name the substance X. (b) How does substance X make the detection of leakage of LPG easy?
Answer:
(a) Substance X is ethyl mercaptan (C2 H5 SH). (b) Ethyl mercaptan is a pungent substance and hence easy to detect.
Page No 132:
Question 40:
The pollution of air caused by burning petroleum fuels (like petrol and diesel) in vehicles can be controlled by fitting a device X in the exhaust system of vehicles.
(a) Name the device X. (b) How does this device help in controlling air pollution?
Answer:
(a) The device is a 'catalytic converter'. (b) A catalytic converter converts the harmful gases from the exhaust of vehicles into harmless gases. For example, it converts carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxide into nitrogen gas.
Page No 140:
Question 1:
A hydro-power plant converts one form of energy into another. Name the two forms of energy.
Answer:
A hydropower plant converts potential energy (of stored water) into electrical energy by rotating turbines in flowing water.
Page No 140:
Question 2:
What type of energy is possessed by flowing water?
Answer:
Flowing water possesses kinetic energy.
Page No 140:
Question 3:
Flowing water can rotate a turbine. Which type of energy is used up by the turbine?
Answer:
The kinetic energy of flowing water is used to rotate a turbine.
Page No 140:
Question 4:
Name the original source of wind energy.
Answer:
The sun is the original source of wind energy.
Page No 140:
Question 5:
What should be the minimum wind speed for the satisfactory working of a wind-powered electric generator?
Answer:
The minimum wind speed for the satisfactory working of a wind-powered electric generator is 15 km/h.
Page No 140:
Question 6:
Write one use of wind energy (a) in the past (b) at present.
Answer:
(a) In the past, wind energy was used in windmills to pump water from wells and to grind wheat into flour. (b) Nowadays, wind energy is used to generate electricity through wind-powered generators.
Page No 140:
Question 7:
Why is the copper tube of a solar water heater painted black from outside?
Answer:
The copper tube of a solar water heater is painted black from outside so as to collect as much the sun's heat as possible, because a black surface absorbs more heat than a white surface.
Page No 140:
Question 8:
What type of reactions occurring inside the sun produce solar energy?
Answer:
The nuclear fusion reaction that occurs inside the sun produces solar energy.
Page No 140:
Question 9:
Name some of the solar energy devices.
Answer:
Solar cookers, solar water heaters and solar cells are solar energy devices.
Page No 140:
Question 10:
What type of reflector is used in a box-type solar cooker?
Answer:
A plane mirror is used as the reflector in a box-type solar cooker.
Page No 140:
Question 11:
What is the range of temperature which can be achieved in a box-type solar cooker in two to three hours?
Answer:
The range of temperature achieved in a box-type solar cooker in two to three hours is 100°C to 140°C.
Page No 140:
Question 12:
Name the device which converts sunlight into electricity.
Answer:
Solar cells convert sunlight into electricity.
Page No 140:
Question 13:
How much solar energy will be received by 1 m2 area in one hour if the solar constant be 1.4 kW/m2 ?
Answer:
Solar constant = 1.4 kW/m2 = 1.4 kJ/s/m2 1 hour in seconds = 60 ×
60 = 3600 Energy received in one hour = 3600 ×
1.4 kJ/m2 = 5040 kJ/m2
Page No 140:
Question 14:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words: A solar cell converts ……………. energy into ……………. energy.
Answer:
A solar cell converts solar energy into electrical energy.
Page No 140:
Question 15:
(a) What is the difference between a thermal power plant and a hydro power plant? (b) Which of the two causes serious air pollution and how?
Answer:
(a)
| Hydropower plant | Thermal power plant | |
| 1. | A hydropower plant uses flowing water to rotate turbines. | A thermal power plant uses coal, oil or gas to drive turbines. |
| 2. | A hydropower plant does not cause air pollution. | A thermal power plant causes air pollution. |
(b) A thermal power plant causes serious air pollution. This is because, in a thermal power plant, large amounts of fossil fuels are burnt every day to generate electricity.
Page No 141:
Question 26:
(a) What is hydroelectricity? Explain the basic principle of generation of hydroelectricity with the help of a labelled diagram. (b) State two advantages of producing hydroelectricity. (c) State two disadvantages of producing hydroelectricity.
Answer:
(a) Hydroelectricity is the product of a process by which mechanical energy from the flow of water is used to generate electricity.
It works on the principle of conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy. Mechanical energy from the flow of water is used to rotate turbines, which are connected to a dynamo that generates electricity.
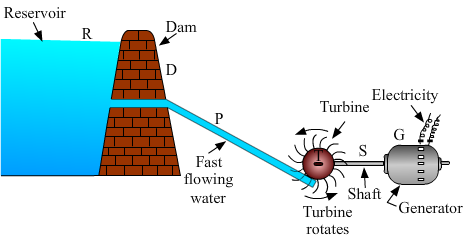
(b) The advantages of hydroelectricity are given below. (1) It does not cause any pollution. (2) It is a renewable form of energy.
© The disadvantages of hydroelectricity are given below. (1) Hydroelectricity plants require the construction of large dams, which affects the ecology of the surroundings. (2) Hydropower plants require water in reservoirs and are dependent on rain for their functioning.
Page No 141:
Question 27:
(a) With the help of a labelled diagram, explain the construction and working of a solar cooker. (b) Why is the solar cooker box painted black from inside? (c) Why is the solar cooker box covered with a glass sheet?
Answer:
(a) A solar cooker is illustrated below.
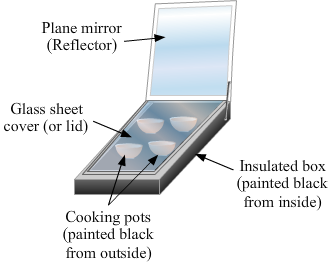
Explanation: A solar cooker is a device in which heat energy from sunlight is trapped inside the cooker using the phenomenon of the greenhouse effect. A solar heating device such as a solar cooker uses a reflector to reflect sunlight to a small area where the cooking container is placed. The light from the sun is focussed on the container, which gets heated, cooking the food.
(b) A solar cooker box is painted back from the inside so that light is not reflected and the maximum absorption takes place.
© A solar cooker is covered with a glass sheet to produce a greenhouse effect inside the cooker box. The greenhouse effect is a phenomenon by which heat is trapped.
Page No 141:
Question 28:
(a) What is wind? What type of energy is possessed by wind? (b) Explain how, wind energy can be used to generate electricity. Illustrate your answer with the help of a labelled diagram. (c) State two advantages of using wind energy for generating electricity. (d) Mention two limitations of wind energy for generating electricity.
Answer:
(a) Wind is the flow of air and is a source of energy. It possesses mechanical energy.
(b) Wind is the flow of air and possesses mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is used to rotate wind turbines, which are connected to electricity generators. See the diagram given below.
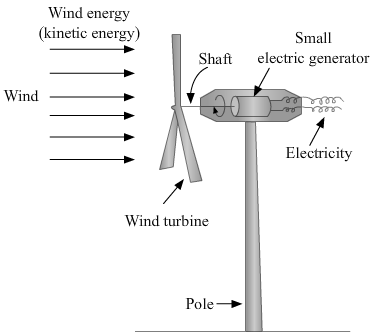
© The advantages of wind energy are as follows. (1) Wind is a clean source of energy. It does not cause any pollution. (2) It is a renewable source of energy.
(d) The limitations of wind energy are as follows. (1) The production of energy depends on the flow of air. It varies during different times of the day and is seasonal. (2) The initial capital cost is very high.
Page No 141:
Question 29:
A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on:
(a) a sunny day (b) a cloudy day (c) a hot day (d) a windy day
Answer:
(b) a cloudy day
A solar water heater receives energy from the sun, but the sun does not appear on a cloudy day. Therefore, a solar water heater does not receive energy on a cloudy day and cannot heat up water.
Page No 141:
Question 30:
At a hydro power plant:
(a) kinetic energy possessed by stored water is converted into electrical energy (b) electricity is extracted from water (c) water is converted into steam to turn turbines and produce electricity. (d) potential energy possessed by stored water is converted into electricity.
Answer:
(d) potential energy possessed by stored water is converted into electricity
A hydropower plant uses running water to rotate turbines.
Page No 141:
Question 31:
The part of box-type solar cooker which is responsible for producing greenhouse effect is:
(a) plane mirror reflector (b) black coating inside the box (c) glass sheet cover (d) utensils placed in the cooker box
Answer:
© glass-sheet cover
The part of a box-type solar cooker that is responsible for producing a greenhouse effect is its glass-sheet cover.
Page No 141:
Question 32:
Solar cells are made of:
(a) conductors (b) insulators (c) semi-conductors (d) super-conductors
Answer:
© semi-conductors
Solar cells are made of semiconductors.
Page No 141:
Question 33:
The value of solar constant is:
(a) 1.4 kWh (b) 1.4 kW/m (c) 1.4 kW/m2 (d) 1.4 kW/m3
Answer:
© 1.4 kW/m2
The value of the solar constant is 1.4kW/m2 .
Page No 141:
Question 34:
The radiations present in sunlight which make a solar cooker work are:
(a) visible light rays (b) ultraviolet rays (c) cosmic rays (d) infrared rays
Answer:
(d) infrared rays
Infrared rays make sunlight warm. The warmth of sunlight is used in a solar cooker.
Page No 141:
Question 35:
In order to make an efficient solar cooker, the cover of cooker box should be made of:
(a) transparent plastic sheet (b) shining aluminium sheet (c) butter paper sheet (d) transparent glass sheet
Answer:
(d) transparent glass sheet
A transparent glass sheet does not allow the incident sun's heat to be reflected back.
Page No 141:
Question 16:
Compare the sun and the fossil fuels as the sources of energy.
Answer:
| Fossils fuels | The sun |
1. Fossils fuels are formed from the remains of dead plants and animals. 2. The burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution. 3. Fossils fuel are non-renewable sources of energy. |
Inside the sun, nuclear fission occurs, which produces enormous amounts of heat. The use of solar energy does not cause any air pollution. Sunlight is a renewable source of energy. |
Page No 141:
Question 17:
What kind of mirror, concave, convex or plane, would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Answer:
A concave mirror is best suited for use in a solar cooker because it converges a large amount of the sun's heat rays at its focus, because of which a high temperature is produced in the focus area.
Page No 141:
Question 18:
(a) Name that part of a box-type solar cooler which allow the sun's heat rays to enter the box but does not allow inside heat to go out. (b) Explain why, a plane mirror reflector is used in a box-type solar cooker.
Answer:
(a) A glass-sheet cover in a box-type solar cooker allows the sun's heat to enter the box but does not allow the heat inside to go out. (b) A plane mirror reflects the sun's rays in the form of a strong beam of light. This property of a plane mirror is used in a box-type solar cooker.
Page No 141:
Question 19:
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a solar cooker?
Answer:
The advantages of using a solar cooker are as follows. a) It does not require fuels such as coal, kerosene and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). b) It does not produce harmful smoke that pollutes the air. c) It does not spoil the nutrients in food. d) It allows for the preparation of more than one item at a time.
The disadvantages of using a solar cooker are as follows. a) It cannot be used to cook food at night.
b) A cloudy sky affects its working.\\
c) The direction of the reflector has to be changed from time to time. d) It cannot be used for baking.
Page No 141:
Question 20:
(a) What is a solar cell? Draw the labelled diagram of a solar cell. (b) Name the semi-conductor material which is usually used for making solar cells. (c) Write the uses of solar cells.
Answer:
(a) A solar cell is an electrical device that converts light energy into electrical energy. 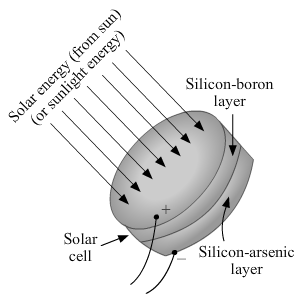
(b) A semiconductor material, such as silicon, is used in making solar cells.
© The uses of solar cells are given below. (1) To provide electricity to electrical appliances such as bulbs and geysers (2) To generate power in a space station
Page No 141:
Question 21:
State the advantages and disadvantages of using solar cells.
Answer:
The advantages of solar cells are that they do not have moving parts, they require no maintenance and they work with any kind of light-focussing devices. Moreover, they can be used even in remote areas.
The disadvantages of solar cells are that they require an expensive special grade of silicon or silver wire, they have low efficiency and they convert only 25 per cent of light falling on them into electricity.
Page No 141:
Question 22:
What is a solar cell panel? For what purpose is it used? State its two main advantages.
Answer:
A solar cell panel consists of a large number solar cells joined together in a series in a definite pattern.
Solar cell panels are used to provide electricity in remote and inaccessible rural areas.
The advantages of solar cell panels are given below. (a) They provide a larger amount of electricity than a single cell and hence can be used to operate TVs and water pumps. (b) The electricity produced by solar cell panels can be stored in batteries and used at night.
Page No 141:
Question 23:
(a) What is solar constant? What is the value of solar constant? (b) If the energy received by 5 m2 area in 10 minutes is 4200 kJ, calculate the value of solar constant.
Answer:
(a) The amount of solar energy received per second on one square metre area of the near-earth space at an average distance between the sun and the earth is called the solar constant. Its value is 1.4 kJ/s/m2 or 1.4 kW/m2 .
(b) Area = 5 m2 Time = 10 min = 10 × 60 sec = 600 sec Energy = 4200 kJ Therefore, solar constant = Energy/(Time × Area) = 4200/(5 × 600) kJ/s/m2 = 4200/(3000) kJ/s/m2 =1.4 kJ/s/m2 =1.4 kW/m2
Page No 141:
Question 24:
How has the traditional use of energy of flowing water been modified for our convenience?
Answer:
Before the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, water energy served many purposes, but the methods of using it were not efficient. For example, the flow of water was used for transporting wooden logs and grinding wheat to make flour. Nowadays, water energy is harnessed to produce electricity, which is a better and more efficient use of this form of energy.
Page No 141:
Question 25:
How has the traditional use of energy of wind energy been modified for our convenience?
Answer:
Before the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, wind energy served many purposes, but the methods of using it were not efficient. For example, windmills were used to power smaller mills, such as flour mills and saw mills. Nowadays, wind energy is harnessed to produce electricity, which is a better and more efficient use of this form of energy.