Ch-5 Periodic Classification of Elements - Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur Solutions Part 2
Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur (chemistry) Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification Of Elements are provided here with simple step-by-step explanations. These solutions for Periodic Classification Of Elements are extremely popular among Class 10 students for Science Periodic Classification Of Elements Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the Lakhmir Singh Manjit Kaur (chemistry) Book of Class 10 Science Chapter 5 are provided here for you for free.
Page No 304: Question 27: (a) What is the fundamental difference in the electron configurations between the group 1 and group 2 elements?
(b) On the basis of electronic configuration, how will you identify: (i) chemically similar elements? (ii) the first element of a period?
ANSWER: (a)
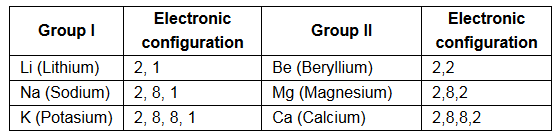
(b) (i) Elements having the same number of valence electrons in their atoms will be chemically similar because the chemical properties of an element depend on the number of electrons present in the outermost shell (valence electrons) of an atom of the element.
(ii) The first element of each period has only one outermost electron. For example, if an element has an electronic configuration of (2,1), we understand that the element belongs to group 1.
Page No 304: Question 28: (a) What is the usual number of valence electrons and valency of group 18 elements of the periodic table? (b) What happens to the number of valence electrons in the atoms of elements as we go down in a group of the periodic table?
ANSWER: (a) The usual number of valence electrons of group 18 elements is 8. Therefore, the valency of the group 18 elements is: 8-8=0.
(b) On moving down in a group of the periodic table, the number of valence electrons in the atoms of elements remains the same.
Page No 304: Question 29: (a) What is the main characteristic of the last elements in the periods of the periodic table? What is the general name of such elements? (b) What is the number of elements is : (a) 1st period, and (b) 3rd period, the modern periodic table?
ANSWER: (a) The last elements in the periods of the periodic table have their valence shells completely filled with electrons. They are known as noble or inert gases. Their valency is zero.
(b) The number of elements in (a) 1st period is 2 and (b) 3rd period is 8 in the modern periodic table.
Page No 304: Question 30: (a) How does the atomic size vary on going down from top to bottom in a group of the periodic table? Why does it vary this way? (b) Lithium, sodium and potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements? Explain your answer.
ANSWER: (a) The atomic size increases on moving from top to bottom in a group of the periodic table. This is because, on moving down in a group, new shells of electrons are added.
(b) Lithium, sodium and potassium are all metals which belong to group 1, and have 1 valence electron in their atoms. They all have the same electronic configuration. Therefore, each element shows similar chemical properties when reacting with water and liberates hydrogen gas.
Page No 304: Question 31: (a) How does the tendency to lose electrons change as we go down in group 1 of the periodic table? Why does it change this way? (b) How does the tendency to gain electrons change as we go down in group 17 of the periodic table? Why does it change this way?
ANSWER: (a) In group 1 of the periodic table, the tendency to lose electrons increases on moving from top to bottom. This happens because an electron shell gets added at every stage and, the atomic radius increases. As the size of the atom increases, the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus increases. This reduces the nuclear attraction force, causing the atom to lose its valence electrons easily, and form cations.
(b) In group 17 of the periodic table, the tendency to gain electrons decreases on moving from top to bottom. On moving down in a group, an electron shell gets added at every stage. As a result, the atomic radius increases. Since the size of the atom goes on increasing, it becomes difficult for the nucleus to attract the incoming electron, due to which the atom cannot form anions easily.
Page No 304: Question 32: (a) Why does the size of the atoms progressively become smaller when we move from sodium (Na) to chlorine (Cl) in the third period of the periodic table? (b) Helium and neon are unreactive gases. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common?
ANSWER: (a) The size of atoms decreases progressively, on moving from sodium (Na) to chlorine (Cl) in the third period because the atomic number of the elements increases. Likewise, the number of electrons and protons in the atoms also increases. As the positive charges on the nucleus increase, the outermost electrons are held more tightly by the nucleus. Therefore, the size of the atom decreases.
(b) The atoms of helium and neon have their valence shells completely filled with electrons. The number of valence electrons is 8. So, they do not show any reactivity.
Page No 304: Question 33: (a) In the modern Periodic Table, why does cobalt with higher atomic mass of 58.93 appear before nickel having lower atomic mass of 58.71? (b) Why could no fixed position be given to hydrogen in Mendeleev's periodic table?
ANSWER: (a) In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged according to their increasing atomic number. The atomic numbers of cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni) are 27 and 28, respectively. Therefore, although cobalt (Co) has higher atomic mass, it appears before nickel (Ni) in the periodic table.
(b) Mendeleev's periodic law could not assign a fixed position to hydrogen in the periodic table because hydrogen resembled both alkali metals (Group 1) and halogens (Group 17) in some of its properties. Hydrogen reacts with metals to form ionic compounds called hydrides and also with non-metals to form covalent compounds.
Page No 304: Question 34: (a) What are the periods and groups in a periodic table? Give two characteristics of each. (b) In terms of electronic configurations, explain the variation in the size of the atoms of the elements belonging to the same period and same group. © Given alongside is a part of the periodic table. As we move vertically downward from Li to Fr:
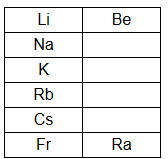
(i) What happens to the size of atoms? (ii) What happens to their metallic character? (d) Name two properties of elements whose magnitudes change when going from top to bottom in a group of the periodic table. In what manner do they change? (e) Rewrite the following statement after correction, if necessary: Groups have elements with consecutive atomic numbers. ANSWER: (a) Periods are the horizontal rows of elements and Groups, the vertical columns of elements in the periodic table.
Characteristics of groups: 1. Elements of the same group have the same number of valence electrons. 2. Elements of the same group exhibit similar chemical properties as they have the same valency.
Characteristics of periods: 1. Elements of the same period have the same number of shells. 2. The valency of elements in the same period changes, and therefore, the elements in a period exhibit different chemical properties.
(b) The size of the atom increases on moving from top to bottom in the same group because at every step, new shells of electrons are added. In a period, the size of the atom decreases on moving from left to right. This is because the atomic number of the elements increases on moving from left to right. Thereby, the number of electrons and protons also increases. Due to the increment in the number of protons, the nuclear charge also increases and the electrons get held more tightly to the nucleus.
© When we move vertically down from Li to Fr: (i) The size of the atom increases. (ii) The metallic character of the elements increases.
(d) On moving from top to bottom in a group , the size of the atoms and the metallic character of the elements increases.
(e) Periods have elements with consecutive atomic numbers.
Page No 304: Question 25: (a) Explain why: (i) All the elements of a group have similar chemical properties. (ii) All the elements of a period have different chemical properties.
(b) The atomic radii of three elements X, Y and Z of a period of the periodic table are 186 pm; 104 pm and 143 pm respectively. Giving a reason, arrange these elements in the increasing order of atomic numbers in the period.
ANSWER: (a) (i) All the elements of a group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer most shell. (ii) All the elements of a period have different chemical properties because the number of valence electrons for each varies.
(b) The elements in the increasing order of atomic numbers in the period is X
Page No 305: Question 35: (a) Explain why, the first period of the modern periodic table has only two elements whereas second period has eight elements (b) Why do elements in the same group show similar properties but the elements in different groups show different properties? © For each of the following triads, name the element with the characteristics specified below:

(d) State one reason for keeping fluorine and chlorine in the same group of the periodic table. (e) What are the merits of the modern periodic table of elements? ANSWER: (a) The first period has only two elements because the first shell (K shell) can take a maximum of only two electrons. The second period has eight elements because the second shell (L shell) can accommodate a maximum of 8 electrons. The number of elements in a period depends upon the number of shells.
(b) The properties of an element depends on the number of valence electrons present in an atom of the element. Elements of a particular group have similar electronic configurations and the same number of valence electrons in their atoms. Hence, all the elements belonging to a certain group show similar properties. However, the electronic configurations of elements change on moving from left to right in a periodic table. Different groups have different valencies. Therefore, elements in different groups show different properties.
©
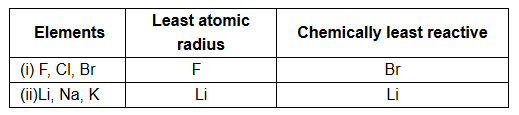
(d) Fluorine and chlorine have a valency of 1 and show similar chemical properties. So, they are placed in the same group.
(e) The merits of the Modern Periodic Table of Elements are as follows: 1. It is based on the atomic number of elements.
2. The modern periodic table clearly explains the reason behind elements showing similar properties in a group and dissimilar properties in different groups.
3. This also explains the reason for the periodicity in the properties of elements.
4. The modern periodic table explains the reason for a repetition in the properties of elements after 2,8,18 and 32 elements.
5. In the modern periodic table, there are no anomalies in the arrangement of elements.
Page No 305: Question 36: (a) What is a group in the periodic table? In which part of a group would you separately expect the elements to have (i) the greatest metallic character (ii) the largest atomic size? (b) In what respects do the properties of group 1 elements differ from those of group 17 elements? Explain with examples by taking one element from each group. © From the standpoint of atomic structure, what determines which element will be the first and which the last in a period of the periodic table? (d) Explain why, the properties of elements are repeated after 2, 8, 18 and 32 elements in the periodic table. (e) What are the advantages of the periodic table?
ANSWER: (a) A group is a vertical column of elements in the periodic table. In a group: (i) The greatest metallic character is expected by elements in the lowest part of the group, as the metallic (electropositive) character increases on going down in a group. (ii) The largest atomic size is found at the bottom of the group, as the atomic size increases on moving down in a group of the periodic table.
(b) Let us explain the properties by taking the example of sodium (Na) in group 1 and chlorine (Cl) in group 17:
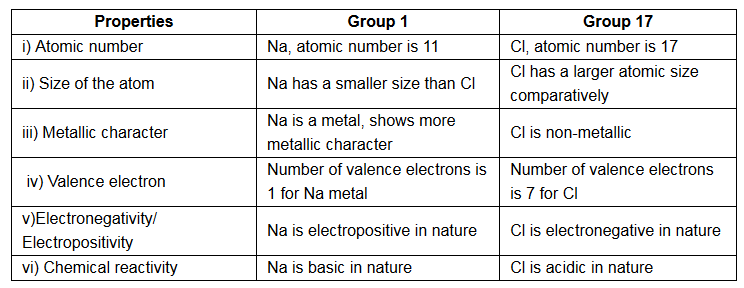
© The number of valence electrons in atoms determines which element will be the first and which the last in a period of the periodic table.
(d) The electronic configurations are repeated because 2, 8, 18 and 32 are the maximum number of electrons that can be placed in the four atomic shells, namely, K, L, M and N. The properties of the elements are repeated after 2, 8, 18 and 32 because the electronic configurations of elements are repeated after 2, 8, 18 and 32.
(e) Advantages of the periodic table: (i) The study of elements and its properties is made easy. (ii) By knowing the position of the element in the periodic table, prediction of the type of compounds that the elements form becomes easy. (iii) The study of chemistry has been made easy in schools and colleges by using the periodic table chart as a teaching-aid.
Page No 305: Question 37: Which of the following statements is not a correct statements about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of the periodic table?
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature. (b) The number of valence electrons increases. © The atoms lose their electrons more easily. (d) The oxides become more acidic.
ANSWER: © The atoms lose their electrons more easily. On moving from left to right in the periodic table, the tendency of an atom to lose electrons decreases.
Page No 305: Question 38: The electronic configuration of the atom of an element X is 2, 8, 4. In modern periodic table, the element X is places in :
(a) 2nd group (b) 4th group © 14th group (d) 8th group
ANSWER: © 14th group Group number = 10 + 4 = 14 Hence, the element X is placed in the 14th group.
Page No 305: Question 39: The atomic number of an element is 20. In modern periodic table, this element is placed:
(a) 2nd period (b) 4th period © 3rd period (d) 1st period
ANSWER: (b) 4th period.
Electronic configuration : K L M N 2 8 8 2 Hence, from the electronic configuration, it is clear that the outermost electron goes into the 4th shell. So, the element would be placed in the 4th period.
Page No 305: Question 40: Five elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic numbers of 2, 3, 7, 10 and 18 respectively. The elements which belong to the same period of the periodic table are:
(a) A, B, C (b) B, C, D © A, D, E (d) B, D, E
ANSWER: (b) B, C, D: B, C and D, with atomic numbers 3,7 and 10 respectively, belong to the same period of the periodic table. This is because the elements B, C and D have the same valence shell (L shell).
Page No 305: Question 41: The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic numbers 9, 11, 17, 12 and 13 respectively. The pair of elements which belongs to the same group of the periodic table is:
(a) A and B (b) B and D © A and C (d) D and E
ANSWER: © A and C Electronic configuration of A (9) : K L 2 7 Electronic configuration of C (17): K L M 2 8 7 Group number of A and B = valence electron + 10 = 7+10 = 17.
Page No 305: Question 42: Which of the following element would lose an electron easily?
(a) Mg (b) Na © K (d) Ca
ANSWER: © K K would lose an electron easily as it is a group 1 metal whose atomic number is greater than that of Na, which also belongs to group 1. Mg and Ca are group 2 metals and the tendency to lose electrons decreases on moving from left to right in a period of periodic table.
Page No 305: Question 43: Which of the following element does not lose an electron easily?
(a) Na (b) F © Mg (d) Al
ANSWER: (b) F F is the element that does not lose an electron easily, as it is a non-metal (halogen) belonging to group 17 of the periodic table.
Page No 305: Question 44: Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the modern periodic table?
(a) group 8 (b) group 2 © group 18 (d) group 10
ANSWER: © Group 18.
The element with an electronic configuration of (2, 8) belongs to group 18 (noble or inert gases) of the periodic table, as the elements in this group have their valence shell completely filled with electrons. Group number = valence shell + 10 = 8+10 = 18.
Page No 305: Question 45: An element which is an essential constituent of all organic compounds belongs to following group of modern periodic table:
(a) group 4 (b) group 14 © group 15 (d) group 16
ANSWER: (b) Group 14. Carbon is the essential constituent of all organic compounds and belongs to Group 14 of the modern periodic table. Electronic configuration of carbon (6): K L 2 4 Group number = valence shell+10 = 4+10 = 14.
Page No 305: Question 46: Which of the following is the valence shell for the elements of second period of the modern periodic table?
(a) M shell (b) K shell © L shell (d) N shell
ANSWER: © L shell. L is the valence shell for elements of the second period of the modern periodic table, since the period number is decided by the number of valence shells.
Page No 305: Question 47: The element which has the maximum number of valence electrons is:
(a) Na (b) P © Si (d) Al
ANSWER: (b) P. Phosphorus (P) has the maximum number of valence electrons, equal to 5. Electronic configuration of P (15): K L M 2 8 5 Sodium (Na) has 1, Silicon has 4 and Aluminium (Al) has 3.
Page No 305: Question 48: The correct increasing order of the atomic radii of the elements oxygen, fluorine and nitrogen is:
(a) O, F, N (b) N, F, O © O, N, F (d) F, O, N
ANSWER: (d) F, O, N The increasing order of the atomic radii of oxygen, fluorine and nitrogen is fluorine, oxygen and nitrogen. This is because the atomic radius decreases from left to right in a period.
Page No 306: Question 49: The atomic numbers of the elements Na, Mg, K and Ca are 11, 12, 19 and 20 respectively. The element having the largest atomic radius is:
(a) Mg (b) Na © K (d) Ca
ANSWER: © K. Potassium (K) with an atomic number of 19 has the largest atomic radius. This is because sodium and potassium are elements of group 1. On moving from top to bottom in a group, the atomic radius increases. Magnesium and calcium are elements of group 2. The size of the atomic radius decreases on moving from left to right in a period of the periodic table
Page No 306: Question 50: Which of the following are the correct characteristics of isotopes of an element? (i) same atomic mass (ii) same atomic number (iii) same physical properties (iv) same chemical properties
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv) (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) © (ii) and (iii) (d) (ii) and (iv)
ANSWER: (d) (ii) and (iv). Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number and the same chemical properties.
Page No 306: Question 51: The correct formula of the oxide of Eka-aluminium element predicted by Mendeleev was:
(a) EaO3 (b) Ea3 O2 © Ea2 O3 (d) EaO
ANSWER: © Ea2 O3 The correct formula for the oxide of eka-aluminium, as predicted by Mendeleev, is Ea2 O3.
Page No 306: Question 52: The element which can from an acidic oxide should be the one whose atomic number is:
(a) 6 (b) 16 © 12 (d) 19
ANSWER: (b) 16. The element which can form an acidic oxide should be the one with atomic number 16. Sulphur has an atomic number of 16 and sulphur oxide is acidic.
Note: Option (a) 6: carbon also forms an acidic oxide but the acidic strength of the oxides of sulphur (16) is greater than that of carbon (6).
Page No 306: Question 53: The element which forms a basis oxide has the atomic number of:
(a) 18 (b) 17 © 14 (d) 19
ANSWER: (d) 19. Potassium (K) forms a basic oxide and has an atomic number of 19. The atomic numbers of 18,17 and 14 correspond to acidic oxides.
Page No 306: Question 54: Which one of the following does not increase while moving down the group of the periodic table?
(a) atomic radius (b) metallic character © valence electrons (d) shells in the atoms
ANSWER: © Valence electrons The number of valence electrons does not increase while moving down the group in the periodic table.
Page No 306: Question 55: On moving from left to right in a period of the periodic table, the atomic number of elements increases. What happens to the size of atoms of elements on moving from left to right in a period?
(a) increases (b) decreases © remain the same (d) first increases then decreases
ANSWER: (b) Decreases. The size of the atom decreases on moving from left to right in a period of the periodic table. With an increment in the atomic number, both the proton number and the nuclear positive charge increase. As the nucleus attracts the outermost electron, the size of the atom decreases.
Page No 306: Question 56: Which of the following set of elements is written correctly in the order of their increasing metallic character?
(a) Mg, Al, Si (b) C, O, N © Na, Li, K (d) Be, Mg, Ca
ANSWER: (d) Be, Mg, Ca. Be, Mg and Ca are elements of group 2, written in order of their increasing metallic character. On moving down in the group, the metallic character increases.
Page No 306: Question 57: The atomic numbers of the three elements X, Y and Z are 2, 6 and 10 respectively. (i) Which two elements belong to the same group? (ii) Which two elements belong to the same period? Give reasons for your choice.
ANSWER: (i) In order to determine the group of the elements, let us first write down the electronic configuration of the elements from their atomic numbers.

(ii) The elements which have the same valence shell belong to the same period in the periodic table. We can see from the electronic configurations of Y and Z , that they have the same valence shell (L). Therefore, elements Y and Z belong to the same period in the periodic table.
Page No 306: Question 58: An atom has the electron structure of 2, 7. (a) What is the atomic number of this atom? (b) To which of the following would it be chemically similar? 7 N, 15 P, 17 Cl, 18 Ar © Why would you expect it to be similar?
ANSWER: (a) The atomic number of the atom is 9 (electronic configuration 2, 7), since it is the sum total of the electrons present in an atom.
(b) The atom would be chemically similar to 17 Cl (electronic configuration 2,8,7).
© They are similar because both have the same number of valence electrons (7) in their atoms.
Page No 306: Question 59: Consider the following elements: 20 Ca, 8 O, 18 Ar, 16 S, 4 Be, 2 He Which of the above elements would you expect to be:
(i) very stable? (ii) in group 2 of the periodic table? (iii) in group 16 of the periodic table?
ANSWER: (i) 18 Ar and 2 He are very stable elements, as their valance shells are completely filled. They belong to the group of inert or noble gases.
(ii) 20 Ca and 4 Be are the two elements that belong to group 2 of the periodic table. This is because their valency is 2 and they are electropositive.
(iii) 8 O (2,6) and 16 S (2,8,6) are the two elements that belong to group 16 of the periodic table. Group number = Valence shell + 10 = 6 + 10 = 16
Page No 306: Question 60: In each of the following pairs, choose the atom having the bigger size:
(a) Mg (At. No.12) or Cl (At. No.17) (b) Na (At. No. 11) or K (At. No. 19)
ANSWER: (a) Mg has a bigger size than Cl because the atomic size decreases on moving from left to right in a period of the periodic table. Mg and Cl belong to group 3 of the periodic table.
(b) K has a bigger size than Na because the atomic size increases on going down in a group of the periodic table. Na and K belong to group 1 of the periodic table.
Page No 306: Question 61: The atomic numbers of three elements A, B and C are given below:
Element Atomic number A 5 B 7 C 10
(i) Which element belongs to group 18? (ii) Which element belongs to group 15? (iii) Which element belongs to group 13? (iv) To which period/periods do these elements belong? ANSWER: (i) Element C belongs to group 18. Electronic configuration of element C (10) = 2,8 Therefore, group number = valence shell + 10 = 8+10 = 18.
(ii) Element B belongs to group 15. Electronic configuration of element B (15) = 2,8,5 Therefore, group number = valence shell + 10 = 5+10 = 15.
(iii) Element A belongs to group 13. Electronic configuration of element A (5) = 2,3 Therefore, group number = valence shell + 10 = 3+10 = 13.
(iv) The elements A, B and C all belong to period 2 because all three have the same valence shell, i.e, L.
Page No 306: Question 62: An element X belongs to 3rd period and group 2 of the periodic table. State:
(a) number of valence electrons (b) valency © metal or non-metal (d) name of the element
ANSWER: (a) The element X has 2 valence electrons because it belongs to group 2.
(b) Since the number of valence electrons and the valency of group 2 elements is 2, the valency of element X is 2.
© Group 2 is on the left side of the periodic table which consists of metals. Therefore X is a metal.
(d) The name of the element is Magnesium (Mg), since X belongs to group 2 and the 3rd period.
Page No 307: Question 63: The following diagram shows a part of the periodic table in which the elements are arranged according to their atomic numbers. (The letters given here not the chemical symbols of the elements):
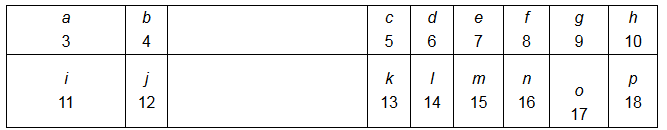
(i) Which element has a bigger atom, a or f? (ii) Which element has a higher valency, k or o? (iii) Which element is more metallic i or k? (iv) Which element is more non-metallic, d or g? (v) Select a latter which represents a metal of valency 2. (vi) Select a letter which represents a non-metal of valency 2. ANSWER: (i) Element a has a bigger atom. In the periodic table, the atomic radius of the element decreases on moving from left to right in a period.
(ii) k has a higher valency.
Electronic configuration of k : K L M 2 8 3 Therefore, valency for k = valence electron of K = 3
Electronic configuration of o: K L M 2 8 7 Therefore, valency for o = 8 - valence electron of o = 8 - 7 = 1
(iii) The element i is more metallic because i belongs to the left side and group 1 of the periodic table. On moving from left to right in a period, the metallic character decreases.
(iv) The element g is more non-metallic, because the non-metallic character increases on moving from left to right in a period.
(v) The elements b or j are metals with a valency of 2 as they have 2 valence electrons and are placed on the left side of periodic table.
(vi) The elements f or n are metals with a valency of 2 .
Electronic configuration of f : K L 2 6 Valency of f = 8 - valence electron = 8 - 6 = 2
Electronic configuration of n : K L M 2 8 6 Valency of n = 8 - valence electron = 8 - 6 = 2
Page No 307: Question 64: An element X is in group 2 of the periodic table: (a) What will be the formula of its chloride? (b) what will be the formula of its oxide?
ANSWER: (a) An element X in group 2 has a valency of 2. We know that chlorine has 7 valence electrons. Therefore, the valency of chlorine Cl is 1, that is, (8 - 7). Now, when one atom of X combines with two atoms of Cl, an ionic compound of the formula XCl2 is formed.
(b) We know that oxygen has 6 valence electrons and needs 2 more electrons to complete its octet. Therefore, the valency of oxygen O is 2, that is, (8 - 6). Both X and O have the same valency. When one atom of X combines with one atom of O, an ionic compound of the formula XO is formed.
Page No 307: Question 65: An element Y is in second period and group 16 of the periodic table:
(i) Is it a metal or non-metal? (ii) What is the number of valence electrons in its atom? (iii) What is its valency? (iv) What is the name of the element? (v) What will be the formula of the compound formed by Y with sodium?
ANSWER: (i) The element Y is a non-metal as all the elements of group 16 are non-metals.
(ii) The number of valence electrons of the element = Group number - 10 = 16-10 = 6. (iii) Valency of Y = 8- number of valence electrons = 8 - 6 = 2. (iv) The name of the element is oxygen as it is the first element in group 16.
(v) Sodium is a group 1 element with a valency of 1. The valency of Y is 2. Therefore, when two atoms of sodium (Na) combine with one atom of Y, the formula of the resulting ionic compound is Na2Y.
Page No 307: Question 66: (a) As element X has mass number 40 and contains 21 neutrons in its atom. To which group of the periodic table does it belong? (b) The element X forms a compound X2Y. Suggest an element that Y might be and give reasons for your choice.
ANSWER: (a) X belongs to Group 1. The mass number of element X is 40 and the number of neutrons in its atom is 21. In order to find out the group to which the element belongs, we need to know the atomic number of the element. Once we know the atomic number of the element, the electronic configuration and valency can be determined. Atomic number = Mass number - Number of Neutrons. Atomic number = 40-21 =19 The electronic configuration of X is 2,8,8,1. The number of valence electrons in X is 1. Therefore, the valency of element X is 1. We know that group 1 elements have a valency of 1.
(b) Y can be oxygen because oxygen has a valency of 2. As X is monovalent, Y has to be divalent in order to form the compound X2Y.
Page No 307: Question 67: An element X combines with oxygen to form an oxide XO. This oxide is electrically conducting.
(a) How many electrons would be there in the outermost shell of the element X? (b) To which group of the periodic tables does the element X belong? © Write the formula of the compound formed when X reacts with chlorine.
ANSWER: (a) The element X is electrically conductive. Therefore, it is a metal. In the case of compound XO, both the elements are divalent, since the valency of oxygen is 2. Therefore, the valency of X should also be 2.
(b) We can conclude that X belongs to Group 2. Since the valency of the element X is 2 and it is showing electrical conductivity, therefore, it is a metal.
© The formula of the compound formed is XCl2, since chlorine is a group 17 element with 7 valence electrons. It has a valency of 1. Therefore, when one atom of X combines with two atoms of chlorine (Cl), an ionic compound of the formula XCl2 is formed.
Page No 307: Question 68: An element A has an atomic number of 6. Another element B has 17 electrons in its one neutral atom.
(a) In which groups of the periodic table would you expect to find these elements? (b) what type of bond is formed between A and B? © Suggest a formula of the compound formed between A and B.
ANSWER: (a) Element A has an atomic number of 6, so its electronic configuration is 2,4 (having 4 valence electrons). Therefore, the group number for element A = valence shell + 10 = 4+10 =14. Hence, the group number for element A is 14.
Element B has 17 electrons in its neutral atom. Its electronic configuration is 2,8,7. Therefore, the group number of element B = valence shell + 10 = 7 + 10 = 17. Hence, the group number for element B is 17.
(b) When two non-metals A and B combine, a covalent bond is formed, since group 14 elements and group 17 elements are all non-metallic in nature.
© When one atom of A combines with four atoms of B, a covalent compound with the formula AB4 is formed. This is because the element A has a valency of 4 and element B has a valency of 1.
Page No 307: Question 69: The elements A, B, C and D belong to groups 1, 2, 14 and 17 respectively of the periodic table. Which of the following pairs of elements would produce a covalent bond?
(i) A and D (ii) C and D (iii) A and B (iv) B and C (v) A and C
ANSWER: (iii) C and D will produce a covalent bond.
The elements C and D belong to group 14 and group 17, respectively. We know that groups 14 and 17 consist of elements that are non-metallic in nature. When two non-metals combine, sharing of electrons takes place, which further results in the formation of a covalent bond.
Page No 307: Question 70: An element X from group 2 reacts with element Y from group 16 of the periodic table.
(a) What is the formula of the compound formed? (b) What is the nature of bond in the compound formed?
ANSWER: (a) An element X from group 2 has a valency of 2. An element Y from group 16 has a valency of 2. As both the elements are divalent, an atom of X combines with an atom of Y to form a compound with the formula XY.
(b) The nature of the bond in the compound is ionic, since the element X is a metal as it is from group 2. The element Y is a non-metal as it is from group 16. When a metal combines with a non-metal, a transfer of electrons takes place and an ionic bond is formed.
Page No 307: Question 71: A metal X is in the first group of the periodic table. What will be the formula of its oxide?
ANSWER: The elements in the first group of the periodic table have a valency of 1. As the metal X is in the first group, its valency is 1. We know that the valency of oxygen is 2 because it needs two electrons to complete its outer shell of 8. From this, we can conclude that two atoms of metal X will combine with one atom of oxygen to form an oxide X2 O. Therefore, the formula of the oxide of metal X is X2 O.
Page No 307: Question 72: An element A from group 14 of the periodic table combines with an element B from group 16.
(i) What type of chemical bond is formed? (ii) Give the formula of the compound formed.
ANSWER: (i) The resulting compound is a covalent compound since the elements of group 14 and group 16 are non-metals. Therefore, when a non-metal A from group 14 combines with a non-metal B from group 16, electrons are shared between their atoms and a covalent bond is formed.
(ii) Element A belongs to group 14 and has 4 valence electrons, and element B belongs to group 16 and has 6 valence electrons. Therefore, when 1 atom of element A combines with 2 atoms of element B, sharing of electrons takes place and the resultant compound will have the formula AB2.
Page No 307: Question 73: An element X from group 2 of the periodic table reacts with an element Y from group 17 to form a compound.
(a) What is the nature of the compound formed? (b) State whether the compound formed will conduct electricity or not. © Give the formula of the compound formed. (d) What is the valency of element X? (e) How many electrons are there in the outermost shell of an atom of element Y?
ANSWER: (a) The resulting compound is an ionic compound since the elements of group 2 are metals and those of group 17, non-metals. When a metal reacts with a non-metal, electrons get transferred from the metallic atoms to the non-metallic atoms, and an ionic bond is formed.
(b) Yes, it will conduct electricity because an ionic compund has formed.
© Element X belongs to group 2 and its valency is 2. Element Y is from group 17 and its valency is 1. So, one atom of X combines with two atoms of Y to give a compound of the formula XY2.
(d) The valency of the element X is 2 because it belongs to group 2.
(e) Group 17 elements have seven valence electrons in their atoms. Group number = valence electron+10 Valence electron = Group number - 10 = 17-10 = 7.
Page No 308: Question 74: The following diagram shows a part of the periodic table containing first three periods in which five elements have been represented by the letters a, b, c, d and e (which are not their chemical symbols):
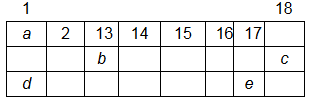
(i) Select the letter which represents an alkali metal.
(ii) Select the letter which represents a nobles gas. (iii) Select the letter which represents a halogen. (iv) What type of bond is formed between a and e? (v) What type of bond is formed between d and e? ANSWER: (i) The letter 'd' represents an alkali metal. This is because group 1 elements of the periodic table, except hydrogen, are all alkali metals having 1 valence electron.
(ii) The letter 'c' represents a noble gas. All the group 18 elements are noble gases or inert gases whose valence shells are completely filled with electrons.
(iii) The letter 'e' represents a halogen. Group 17 elements are known as halogens and they have 7 valence electrons.
(iv) A covalent bond is formed between 'a' and 'e'. 'a', the top most element represents hydrogen which is the only non-metal in group 1. Therefore, when a non-metal 'a' forms a compound with another non-metal 'e', sharing of electrons takes place resulting in the formation of a covalent bond.
(v) An ionic bond is formed between 'd' and 'e'. When a metal reacts with a non-metal, a transfer of electrons takes place from the metal to the non-metal and results in the formation of an ionic bond.
Page No 308: Question 75: The elements A, B and C belong to groups 1, 14, and 17 respectively of the periodic table. (a) Which two elements will form a covalent compound? (b) Which two elements will form an ionic compound?
ANSWER: (a) The element B combines with the element C to form a covalent compound. The elements B and C belong to group 14 and group 17, respectively, which are non-metals. Therefore, when two non-metals react with each other, sharing of electrons takes place, which further results in the formation of a covalent bond.
(b) The element A combines with the element C to form an ionic compound. The element A belonging to group 1 is a metal. The element C belonging to group 17 is a non-metal. Therefore, when a metal combines with a non-metal, electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond.
Page No 308: Question 76: Find the neutral atom in the periodic table which has the same number of electrons as K+ and Cl-. What is this number?
ANSWER: Argon is a neutral atom in the periodic table and has the same number of electrons as K+ and Cl-. The atomic number of argon is 18. It has 18 electrons. Potassium (K) has 19 electrons but because it loses one electron, it becomes K+ and has 18 electrons. On the other hand, chlorine (Cl) has 17 electrons but because it gains one electron, it forms Cl- and has 18 electrons.
Page No 308: Question 77: Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electron shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound. This ionic compound is added in a small amount to almost all vegetables and dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature while those of elements E and F are acidic. The oxide of element D is, however, almost neutral. Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(a) To which group or period of the periodic table do these elements belong? (b) What would be the nature of compound formed by a combination of elements B and F? © Which two of these elements could definitely be metals? (d) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state at room temperature? (e) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G be 3 and 7 respectively, write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
ANSWER: (a) The elements belong to the third period of the periodic table, and have the same number of electron shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shells. The number of valence electrons in these elements increases from 1 to 8, on moving from left to right in this period.
(b) When metal B combines with a non-metal F, an ionic compound is formed due to the transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal. This is because in the third period, elements A, B and C are metals, D is a metalliod, and E, F, G and H are non-metals.
© A and B are definitely metals because in the 3rd period, at the extreme left, only metals are placed in the periodic table .
(d) The element H is most likely to be found in a gaseous state at room temperature. This is because the last group elements in the periodic table are all in a gaseous state at room tempearture.
(e) If the number of valence electrons of element C is 3 and those of element G is 7, then 1 atom of element C will combine with 3 atoms of element G to form a compound with the formula CG3.
Page No 308: Question 78: Write the names and symbols of two very reactive metals belonging to group 1 of the periodic table. Explain by drawing electronic structure, how either one of the two metals reacts with a halogen. With which name is the bond formed between these elements known and what is the class of the compound so formed known? State any four physical properties of such compounds.
ANSWER: Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) are the two very reactive metals belonging to group 1 of the periodic table. Let us see the formation of an ionic compound, namely Sodium Fluoride (NaF), when Sodium (Group 1 element) reacts with Fluorine ( Group 17 element). Sodium has 1 electron in its outermost shell whereas Fluorine has 7 electrons. When Sodium and Fluorine react, a transfer of electrons takes place from Sodium to Fluorine and an ionic compound is formed.
The following drawing clearly explains the reaction of Sodium and Fluorine:

Halogens are the non-metal elements which belong to group 17 of the periodic table. Metals are electropositive and have a tendency to lose electrons while non-metals are electronegative and have a tendency to accept electrons. Therefore, when a metal reacts with a non-metal, a transfer of electrons takes place, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond. The resulting compound is called an ionic compound.
Physical properties of Ionic Compounds: 1. Ionic compounds are solids. 2. They have high melting and boiling points. 3. They are generally soluble in water. 4. They conduct electricity in molten state.
Page No 308: Question 79: The non-metal A is an important constituent of our food and most of the fuels around us. A forms two oxides B and C. The oxide B is poisonous whereas oxide C causes global warming.
(a) Identify A, B and C. (b) To which group of periodic table does A belong? © Name another element which is placed in the same group as A.
ANSWER: (a) The non-metal A which is an important constituent of our food and most of the fuels around us is carbon. Carbon combines with oxygen in two ways to form two oxides. When one atom of carbon combines with one atom of oxygen, carbon monoxide (CO), a poisonous gas is formed. And when one atom of carbon combines with two atoms of oxygen, carbon dioxide (CO2) is formed which causes global warming.
(b) Carbon belongs to group 14 of the periodic table.
© Silicon (Si) is another element which is placed in the same group 14 of the periodic table.
Page No 308: Question 80: A non-metal X which is the largest constituent of air combines with hydrogen when heated in the presence of iron as catalyst to form a gas Y. When gas Y is treated with sulphuric acid, it forms a compound Z which is used as a chemical fertiliser.
(a) What are X, Y and Z? (b) To which group of periodic table does X belong? © Name the period of periodic table in which X is placed. (d) Which element is placed just before X in the period? (e) Which element is placed just after X in the period?
ANSWER: (a) Element X is Nitrogen gas (N2) since the largest constituent of air is nitrogen. When nitrogen reacts with hydrogen in the presence of iron as a catalyst, ammonia (NH3) is formed. Therefore, Y is ammonia (NH3). When ammonia reacts with sulpuric acid, ammonium sulphate is formed which is used as a chemical fertilizer. Therefore, Z is ammonium sulphate (NH4)2 SO4.
(b) Nitrogen belongs to group 15 of the periodic table.
© Nitrogen is placed in the second period of the periodic table.
(d) Carbon (C) is placed just before nitrogen in the period.
(e) Oxygen (O) is placed just after nitrogen in the period.